Practice patterns for outlining the axilla and IMC, findings of the RTQA for the ATNEC trial.
Roeum Butt,
United Kingdom
MO-0644
Abstract
Practice patterns for outlining the axilla and IMC, findings of the RTQA for the ATNEC trial.
Authors: Roeum Butt1, Zohal Nabi1, Romaana Mir2, Jack Hills1, Duncan Wheatley3, Indrani Bhattacharya4, Alison Ranger5, Sophie Cramp6, Natalie Hammonds6, Amit Goyal7, Yat Man Tsang8
1RTTQA, Radiotherapy, London, United Kingdom; 2Mount Vernon Cancer Centre, Clinical Oncology, London , United Kingdom; 3Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust, Clinical Oncology, Cornwall, United Kingdom; 4Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust, Clinical Oncology, Cambridge, United Kingdom; 5The Royal Marsden Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Clinical Oncology, London, United Kingdom; 6University of Warwick, Warwick Clinical Trials Unit, Coventry, United Kingdom; 7Royal Derby Hospital, Oncoplastic Breast Surgery, Derby, United Kingdom; 8Mount Vernon Cancer Centre, Specialised Service Delivery, London, United Kingdom
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Breast radiotherapy with regional nodal irradiation including internal mammary chain (IMC) has been suggested to have survival benefits in patients with high-risk breast cancers. This study aims to examine the interobserver variations in regional nodal target volume delineations of breast IMC radiotherapy in the United Kingdom (UK).
Material and Methods
ATNEC is a randomised phase III trial investigating whether axillary treatment can be safely omitted, in early breast cancer patients who have a complete nodal tumour response following neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04109079). As part of the ATNEC quality assurance (QA) programme, each participating clinician was asked to complete a pre-trial outlining benchmark case which included axillary levels 1-4 and IMC nodal (CTVL1-L4 and CTVIMN) delineations. The contours from each clinician’s QA exercise submission were compared against a set of reference contours (the gold standard) which was defined by the trial management group (TMG). Classifications of either having no variation, acceptable variation, or unacceptable variation from trial protocol, were used to assess the benchmark cases. The Dice coefficients (DICE) were calculated for individual CTV volumes against the gold standard. The Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA was performed to detect whether any statistically significant differences in DICE between CTV volume groups followed by Bonferroni-type multiple comparisons.
Results
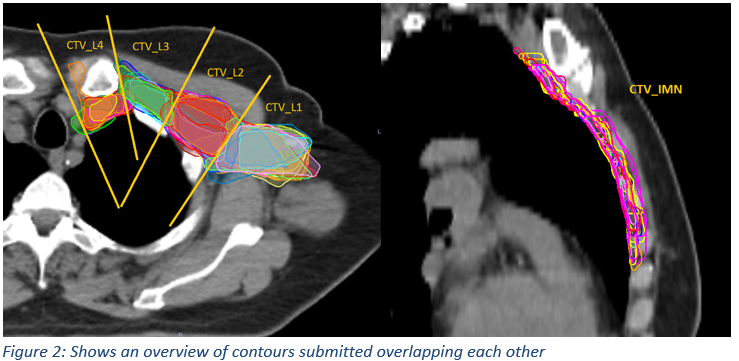
23 clinicians from 14 centres were reviewed between December 2020 to September 2021. 11/23 clinicians had outlines that were classified to have unacceptable variation from the trial protocol. For conformity indices analysis (Fig1), the median DICE of CTV Whole (combining CTVL1-L4 and IMN) was 0.70. Regionally, CTV L1 had the most conformance with a median DICE of 0.65 (SD=0.05) while the CTV IMN showed the worse conformance with a median DICE of 0.52 (SD=0.13). In general, outlining of CTVL1-L4 was consistent (Fig2) with most clinicians identifying the caudal border correctly for CTV L1. For CTV IMN, the caudal border of this nodal group was often over-contoured beyond the cranial extent of the 4th rib. There were statistically significant differences in DICE when comparing between the CTV volume groups (p<0.05). Within Bonferroni-type multiple comparisons, statistically significant differences were detected in whole CTV Whole vs CTV L2, CTV Whole vs CTV IMN and CTV L1 vs CTV IMN (p<0.05).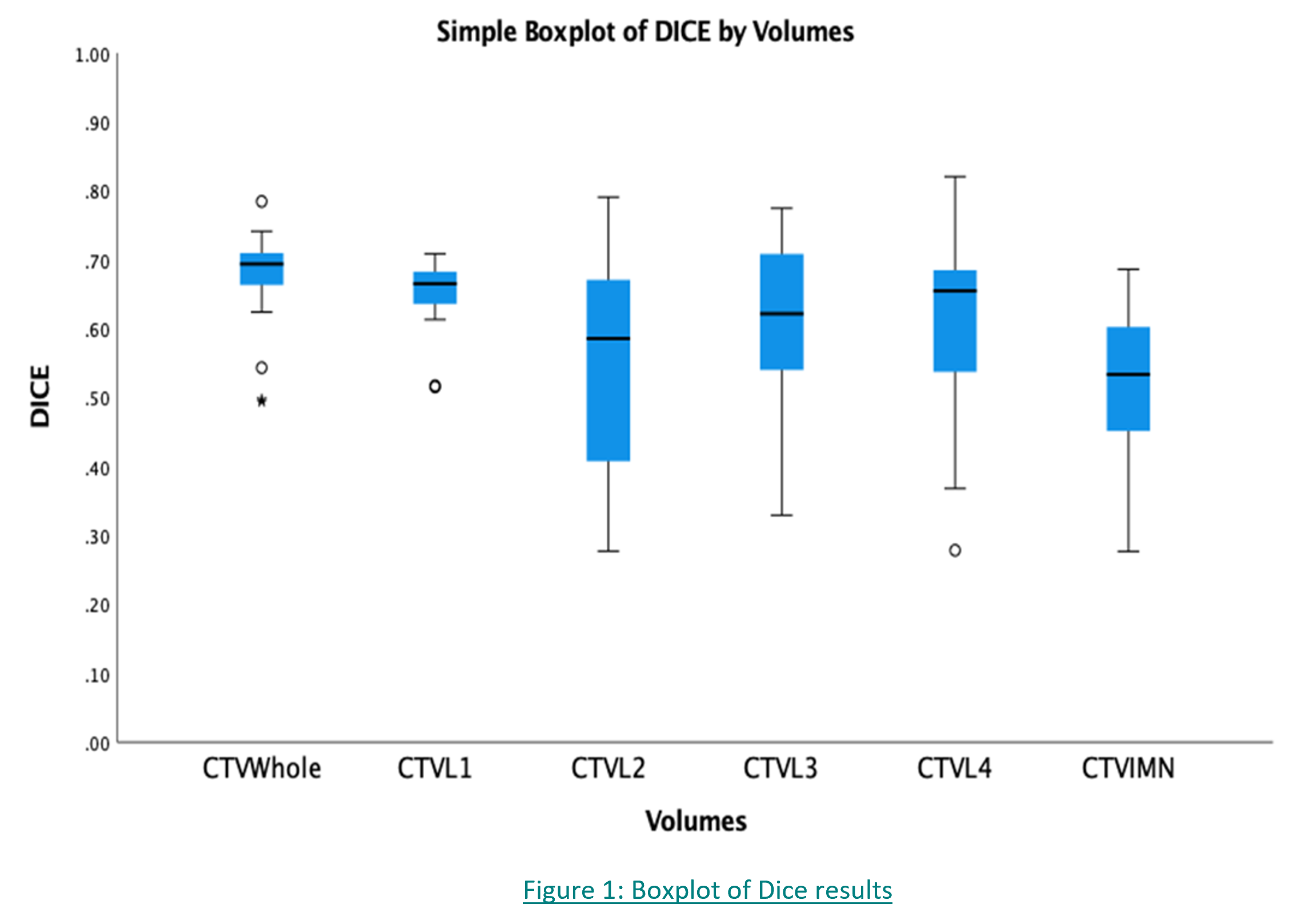
Conclusion
This study suggested that there’s a need for regional assessments of nodal target volume delineations in breast IMC radiotherapy. The QA programme for ATNEC has provided an opportunity to capture interobserver variations of regional axillary lymph nodal delineations within participating centres, in order to provide peer-reviewed feedbacks. Common variations found such as the caudal aspects of the IMN volume quite often extending too far caudal to the recommended guidelines within the trial.