Assessing the inter and intra-fraction changes utilising MR Linac for cervical cancer
Amerah Alshamrani,
United Kingdom
PO-1853
Abstract
Assessing the inter and intra-fraction changes utilising MR Linac for cervical cancer
Authors: Amerah Alshamrani1, Robert Chuter2, Claire Nelder3, Ananya Choudhury4, Lisa Barraclough5, Cynthia Eccles6, Marianne Aznar6, Peter Hoskin7
1The University of Manchester, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, MANCHESTER, United Kingdom; 2Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Clinical Oncology, MANCHESTER, United Kingdom; 3Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Radiotherapy, Manchester, United Kingdom; 4Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Clinical Oncology, MANCHESTER, United Kingdom; 5Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Clinical Oncology, MANCHESTER, United Kingdom; 6The University of Manchester, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, MANCHESTER, United Kingdom; 7The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Clinical Oncology , MANCHESTER, United Kingdom
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Online adaptive radiotherapy based on MR Linac (MRL) can
potentially address inter and intra-fractional changes using images acquired
daily during treatment. We report the intra- and inter-fractional movement for
the first 25 fraction cervical cancer treatment delivered on the MRL in the UK.
Material and Methods
Following institutional approval, a woman with stage FIGO-IIB node-negative
cervical cancer was consented to the MOMENTUM trial (NCT04075305) for 25 fractions
of radiotherapy. Treatment was prescribed according to the EMBRACE II guidelines
using adapt-to-shape (ATS) workflow. A comfortably full bladder was required
for treatment.
Results
22 fractions and 67 MR images were available for review. The mean treatment
time was 68 min (range 51–82 min) from the time the patient entered the room
until the patient left. The median time from the setup image to verif image was
43.5 min (range 31-72 min). The median time from verif image to post-treat
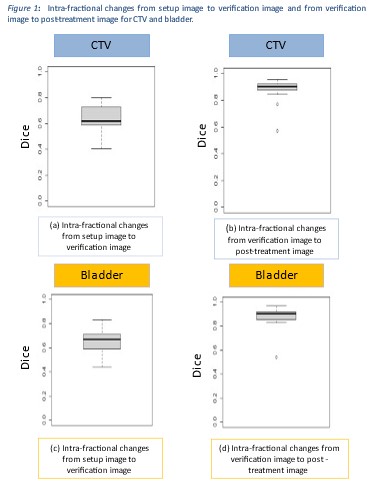
image was 13 min (range 4-40 min). The median intra-fraction DC for the CTV
was 0.62 (range 0.40-0.80) and 0.90 (range 0.57-0.95) for the setup to verif and verif
to post-treat images respectively. The median intra-fractional DC in bladder
volume from setup to verif images and from verif to post-treat images were 0.67
(range 0.44-0.83) and 0.90 (range 0.54-0.97) respectively. Figure 1 shows the
intra-fraction variation from setup to verif and verif to post treat images for
both bladder and CTV. CTV volume changes were greatest in the adaption time,
and smaller during radiation delivery. For inter-fraction movement, median volume
for CTV and bladder were 7.41cm3 (range -4.30-24.92) and -133cm3
(range-382.63-57), respectively. No consistent bladder or CTV volume
patterns were observe.
Conclusion
Drinking protocols were not optimal to keep bladder volume
constant. The low DC value justifies the need for an ATS workflow. Real-time
adaptation based on MRL addressed inter and intra-fraction CTV and bladder
changes by allowing an online correction that improves delineation and treats
on the most updated plan.