Cancer stem cell biomarkers SOX2 and Oct4 in cervical cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy
PO-1359
Abstract
Cancer stem cell biomarkers SOX2 and Oct4 in cervical cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy
Authors: Deep Chakrabarti1, Sumaira Qayoom2, Divya Kukreja1, Madhu Mati Goel2, US Singh2, Mranalini Verma1, Kirti Srivastava1, Madan Lal Bhatt1
1King George's Medical University, Radiotherapy, Lucknow, India; 2King George's Medical University, Pathology, Lucknow, India
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Cancer stem cells(CSCs) are a subpopulation of tumour cells that account for radioresistance. SRY(sex-determining region Y)-box 2(SOX2) and octamer-binding transcription factor 4(Oct4) are transcription factors that have been proposed as biomarkers to identify CSCs in cervical cancers. Data about their clinical implications are limited and contradictory.
Material and Methods
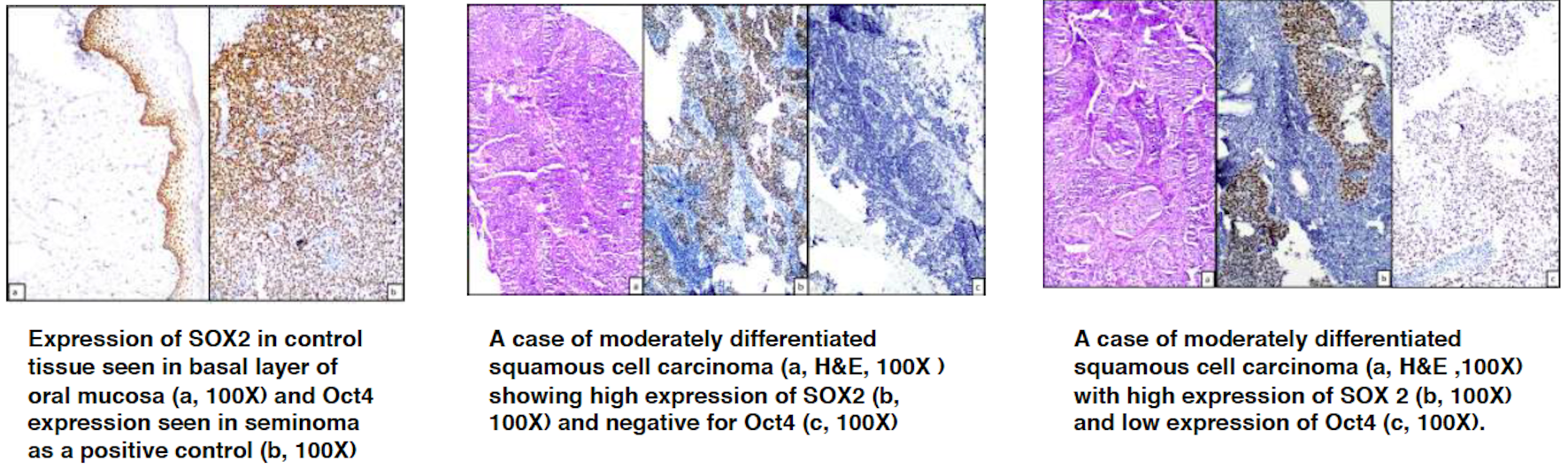
This study included patients of cervical squamous cell carcinoma(FIGO stage IB2-IVA) who received definitive chemoradiotherapy(EBRT with concurrent cisplatin and intracavitary brachytherapy, ICBT) in the year 2017 and were on regular follow-up. Patient particulars were recorded. Tissue biopsy specimens were evaluated for SOX2 and Oct4 expression by immunohistochemistry, quantified by a combined score, product of proportion score(1-<10%positive tumour cells, 2-10-50% cells, 3->50% cells) and intensity score (0-no staining,1-weak,2-moderate, 3-strong). Scores ≤ 4 were considered low expression, while ≥ 6 was high expression.
Results
59 patients were included. Their baseline details were: median age 50 years, most commonly FIGO IIB(64%), moderately-differentiated(81%), keratinising(59%), with necrosis(37%), LVSI(12%), PNI(14%), and tumour infiltrating lymphocytes(TIL)(90%). Most patients (95%) had ≥ FIGO stage IIB disease. The common dose schedule was EBRT of 50Gy followed by 3 ICBT fractions of 7Gy each. The median(IQR) cycles of chemotherapy administered was 4(3–5). Acute reactions were: haematological-49%(Grade III-2%), gastrointestinal-41%(Grade III-3%), genitourinary-7%. Chronic reactions and vaginal stenosis were present in 17%. SOX2 expression(high:low 21:38 patients) and Oct4 expression(high:low 4:55 patients) had a significant inter-relation(P=0.013). There were no significant differences between SOX2/Oct4 expression and clinico-pathological parameters, except TIL(P=0.003) and necrosis(P=0.024) with SOX2 expression.
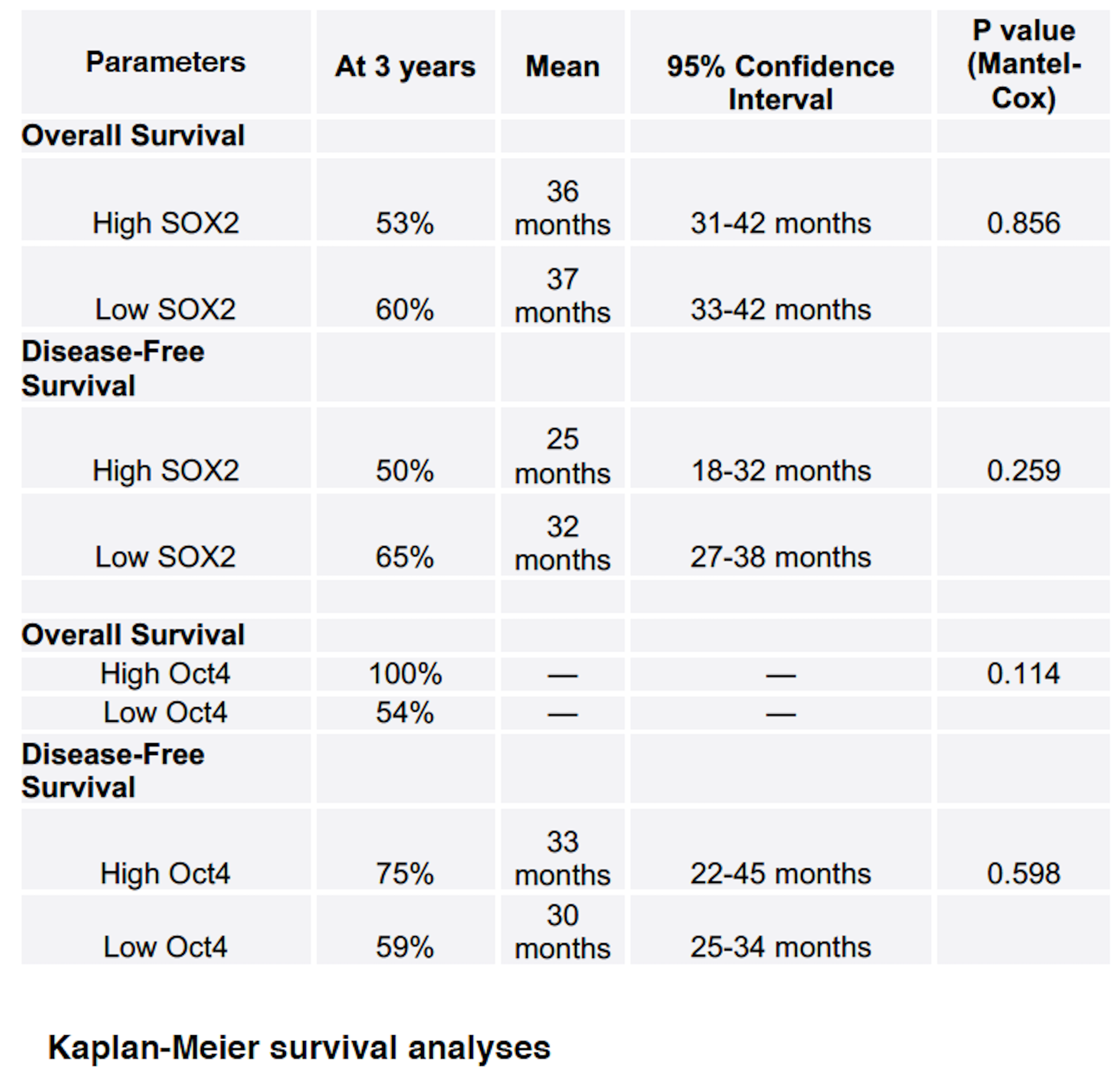
At a median follow-up of 36 months, the three-year OS was 60% in the low SOX2 expression group(Mean(95% CI) 37(33-42) months) and 53% in the high SOX2 expression group(Mean (95% CI) 36(31-42) months)(P=0.856). The three-year OS was 54 % for low Oct4 expression and 100% for high Oct4 expression(P=0.114). On Cox regression, SOX2 expression(P=0.043) and morphology(P=0.032) were the only variables significantly associated with OS.
The three-year DFS was 65% in the low SOX2 expression group(Mean (95% CI) 32(27-38) months) and 50% in the high SOX2 expression group(Mean (CI) 25(18-32) months)(P=0.259). The three-year DFS was 59 % for low Oct4 expression and 75% for high Oct4 expression(P=0.598). On Cox regression, SOX2 expression was the only variable significantly associated with DFS(P=0.038).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrated a trend towards improved OS and DFS with low SOX2 and high Oct4 expression. Future research may focus on validating these biomarkers prospectively in a larger population and intensifying radiotherapy treatment in adverse subgroups, reducing overall treatment time or escalating dose.