Dosimetric evaluation of off-axis fields and angular transmission for the 1.5T MR-Linac
Madelon van den Dobbelsteen,
The Netherlands
PO-1743
Abstract
Dosimetric evaluation of off-axis fields and angular transmission for the 1.5T MR-Linac
Authors: Madelon van den Dobbelsteen1, Wilfred de Vries1, Bram van Asselen1, Bas Raaymakers1, Simon Woodings1, Stijn Oolbekkink1, Sara Hackett1
1UMC Utrecht, Radiotherapy, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
GPUMCD
is a fast dose calculation algorithm used for treatment planning on the Unity
MR-Linac. Treatments for the MR-Linac must be calculated quickly and accurately, especially for two important MR-Linac aspects: off-axis positions, and angular
transmission through the cryostat, couch and MR-coils. Therefore, the aim of
this research is to quantify the largest system related errors for GPUMCD
calculations over the range of clinically-relevant field configurations and
gantry angles.
Results
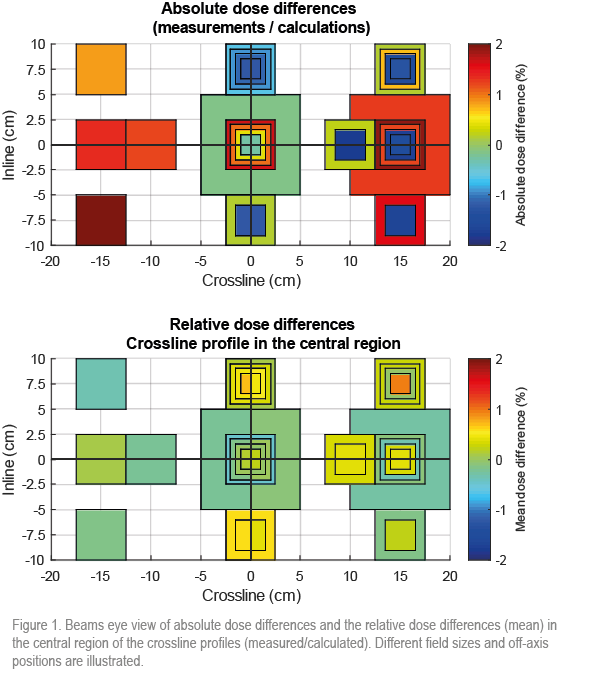
Differences in absolute dose between measurements and
calculations ranging from -1.8% to 2.1% were demonstrated (absolute difference
ranging from -0.8 cGy to 1.0 cGy per 100 MU). For the relative crossline
profiles the dose difference in the central region ranged from -0.5 ± 0.7%
(mean ±
standard deviation) to 1.0 ± 1.6% (see Fig. 1). For the relative inline
profiles the dose difference ranged from -0.6 ± 0.6% to 0.8 ± 1.3%.
For the PDD profiles the dose difference ranged from -0.1 ± 0.4%
to 0.9 ±
0.5%. Positions further from the central axis or different field sizes did
not cause larger dosimetric errors.
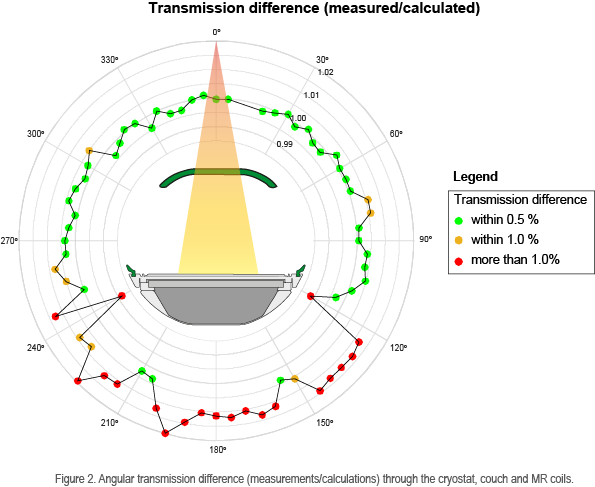
The measured angular transmission generally showed good
agreement with the calculations with transmission differences ranging from
-1.1% to 2.0% (see Fig. 2). Only, relatively large deviations of up to 2% were
observed for beams passing through the edges of the table (120 and 240
degrees).
Conclusion
GPUMCD is a suitable dose calculation algorithm illustrating
similar accuracy of off-axis fields and central axis fields. The largest error
is caused by the couch transmission and the differences in absolute dose,
showing errors up to 2.1%. The relative dose profiles are
showing a lower dosimetric error, with a maximum dose difference of 1% between measurements and calculations.