Real-time hybrid Monte Carlo for dose calculation in proton therapy
PO-1730
Abstract
Real-time hybrid Monte Carlo for dose calculation in proton therapy
Authors: Paula Ibáñez1, Víctor Valladolid2, Amaia Villa-Abaunza2, Andrea Espinosa2, Fernando Arias2, Pablo Galve2, Daniel Sánchez-Parcerisa1, José Manuel Udías1
1University Complutense of Madrid and IdISSC, Nuclear Physics Group and IPARCOS, Madrid, Spain; 2University Complutense of Madrid, Nuclear Physics Group and IPARCOS, Madrid, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Monte Carlo (MC) treatment planning (MCTP) is increasingly demanded for proton verification, especially when heterogeneous tissues are present. However, long computation time limits MCTP for daily clinical applications. We developed a GPU-based Hybrid Monte Carlo for protons (GHMCp) that incorporates all the physics and particle tracking of realistic MC simulations and runs in a fraction of time of a standard MC code.
Material and Methods
GHMCp computes dose distributions, proton fluence, phase spaces and nuclear activations from proton beams within seconds. It incorporates a precalculated database with interactions of protons and their secondary particles in different materials. The database is easily calculated from any MC code, thus predictions from different MC packages can be obtained. Other particles, such as neutrons or alpha particles, can also be tracked. The GPU implementation further increases the speed of the code.
Benchmark MC simulations with PENH-NUCL [1,2] and TOPAS [3] have been used to test GHMCp dose predictions and activation maps in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms. A realistic prostate treatment plan consisting of 1610 pencil beams with energies from 100 MeV to 155 MeV was also simulated. A performance study to assess the speed gain reached with GHMCp has been performed.
Results
Good results have been obtained with the GHMCp code when compared to the reference MC codes in terms of gamma evaluation, with more than 99% voxels fulfilling 3%-3 mm criteria in all homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms and more than 96% voxels in the prostate MCTP. Figure 1 shows dose distribution in the prostate MCTP from PENH-NUCL and GHMCp. GHMCp was proved to be about 10000 times faster than PENH-NUCL (1 core) and 800 times faster than TOPAS (16 cores), for similar statistical uncertainty.
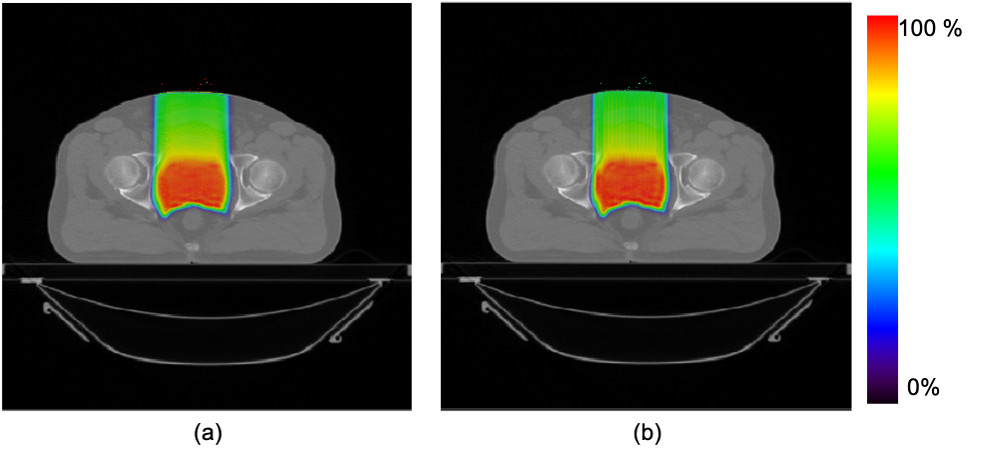
Figure 1. Dose distribution in the prostate MCTP calculated with GHMCp (NVIDIA GeForce GeForce RTX 2080 Ti with 4352 CUDA Cores) (a) and PENH-NUCL (1 core of Intel Xeon CPU E5-2650 0 @ 2.00GHz) (b).
Conclusion
The GHMCp is a fast and versatile computation tool that allows changing from one MC physics to another, the easily incorporation of secondary particles, and that calculates dose and activation maps within seconds, which makes it possible real time calculations and inverse dose planning.