Associations of CT-based radiomics data with disease recurrence in early stage Lung cancer patients
Alexandra Giraldo Marin,
Spain
PO-1775
Abstract
Associations of CT-based radiomics data with disease recurrence in early stage Lung cancer patients
Authors: Alexandra Giraldo Marin1, Marta Ligero2, Alejandro Seoane3, Monica Ramos1, Marc Simo4, Jordi GIralt5, Manuel Escobar6, Perez-Lopez Raquel7
1Vall D´Hebron Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Barcelona, Spain; 2Vall D’Hebron Institute of Oncology, Radiomics Grroup, Barcelona, Spain; 3Vall D´Hebron Hospital, Medical Physics, Barcelona, Spain; 4Vall D´Hebron Hospital, Nuclear Medicine, Barcelona, Spain; 5Vall D´Hebron, Radiation Oncology, Barcelona, Spain; 6Vall D´Hebron, Radiology, Barcelona, Spain; 7Vall D’Hebron Institute of Oncology, Radiomics Group, Barcelona, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
To develop an
association between CT-based radiomics score and clinical prognostic factors
capable of predicting recurrence free survival (RFS) in patients with lung
lesions <5cm
Material and Methods
We analysed
data from 62 patients and 66 lesions treated with SABR from January 2015 to February 2019 in
our institution. 4D
PET-CT images were used for treatment planning, however, only CT images were
used for extracting Radiomics
features. The dose and number of fractions were selected according to our institution protocol.
Retrospectively, a RFS predictive signature was
derived. LASSO-Cox regression was implemented for feature selection and
univariate and multivariate Cox-proportional Hazard regression were implemented
with radiomics features and prognostic clinical factors. Kaplan-Meier (KM)
curves were implemented to evaluate the prognostic value of the signature. A
nomogram was developed for the clinical radiomics model.
Results
Patient’s characteristics are displayed in Table 1. The LASSO-Cox selected three radiomics features as
relevant for RFS prediction from GLCM and GLSZM matrices. The radiomics model
associated with RFS with a Concordance index (CI) of 0.63[0.55- 0.72]. Four
clinical factors were selected by LASSO (body mass index, Karnofsky status,
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and previous thorax irradiation). The
clinical model showed a similar predictive capacity as radiomics only (CI =
0.68[0.57- 0.78]). The integration of radiomics with clinical data improved the
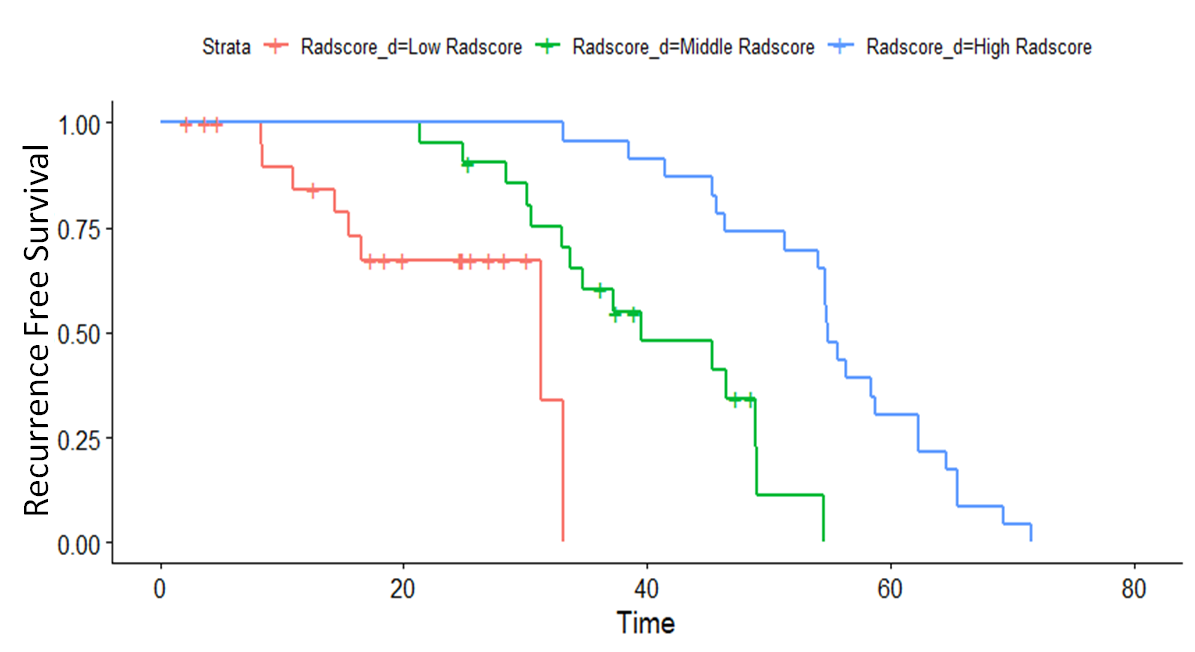
predictive value to a CI=0.84[0.78-0.9]. KM curves showed significant
differences in RFS betwe en low, medium and high clinical radiomics score
(Figure 1).
en low, medium and high clinical radiomics score
(Figure 1).
Conclusion
This study suggest that CT-based radiomics score
associated with prognostic clinical
factors might be a useful tool to improve the prediction of outcomes in
patients with lung lesions treated with radical intention. Validation of the
score is needed.