Inter-fraction prostate bed motion during salvage radiation therapy within the PERYTON-trial
Floor Staal,
The Netherlands
PO-1487
Abstract
Inter-fraction prostate bed motion during salvage radiation therapy within the PERYTON-trial
Authors: Floor Staal1, Charlotte L. Brouwer1, Jorinde Janssen1, Sajee Krishnapillai1, Johannes A. Langendijk1, J. Fred Verzijlbergen2, Igle Jan de Jong3, Robert Jan Smeenk4
1University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Radiation Oncology, Groningen, The Netherlands; 2Radboud University Medical Center, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Nijmegen, The Netherlands; 3University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Urology, Groningen, The Netherlands; 4Radboud University Medical Center, Department of Radiation Oncology, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The PERYTON-trial, a phase
III RCT, investigates the role of hypofractionation in salvage radiotherapy
(SRT) for patients with a biochemical recurrence after prostatectomy. In hypofractionation, accurate dose delivery is
crucial. We aim to analyze the inter-fractional displacement (IFD) of the CTV in
SRT.
Material and Methods
The first 12 patients
treated in the PERYTON-trial were retrospectively analyzed, six patients received the conventional schedule (35x2Gy) and six
patients received the hypofractionated schedule (20x3Gy). The PTV margin used
was 8 mm. Each patient underwent a planning-CT and MRI. Patients were
instructed to show with a comfortably full bladder, no rectal preparation was
applied. Prior to each fraction a CBCT was obtained. CBCTs were matched with
the planning-CT using a bony verification mask, translations only. Rectum and
bladder were contoured for each CBCT. The anterior rectal wall represents the
posterior border of the CTV and the bladder wall represents the anterior border
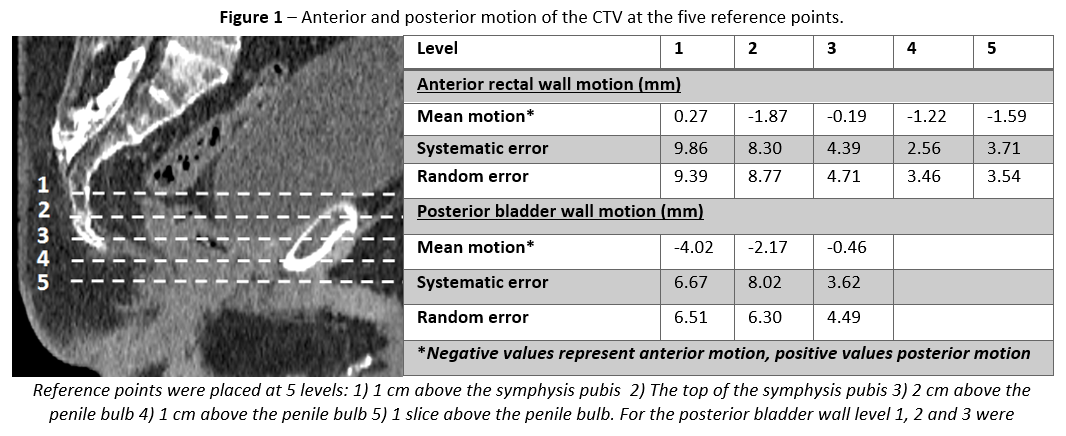
of the CTV. To analyze anterior-posterior (AP) IFD of the CTV, five reference points
of interest were placed at the anterior rectal wall and three at the posterior
bladder wall (Figure 1).
These craniocaudal levels were chosen in
accordance with the guideline of Wiltshire et al. Positive values represent posterior
IFD, negative values anterior IFD. Volume changes and IFD were calculated to
evaluate the coverage within the used PTV margin.
Results
A total of 324 CBCTs
were analyzed. Both treatment arms showed identical changes in (rectum and
bladder) volume and IFD. Treatment time had no influence on volume changes or
IFD. Inter-fractional rectal and bladder volume varied widely, with a median of
+0.7% (IQR -31.7% to +32.1%) and -25.6% (IQR -46.0% to +10.9%), respectively. The
mean IFD, mean population systematic and random errors of all reference points are
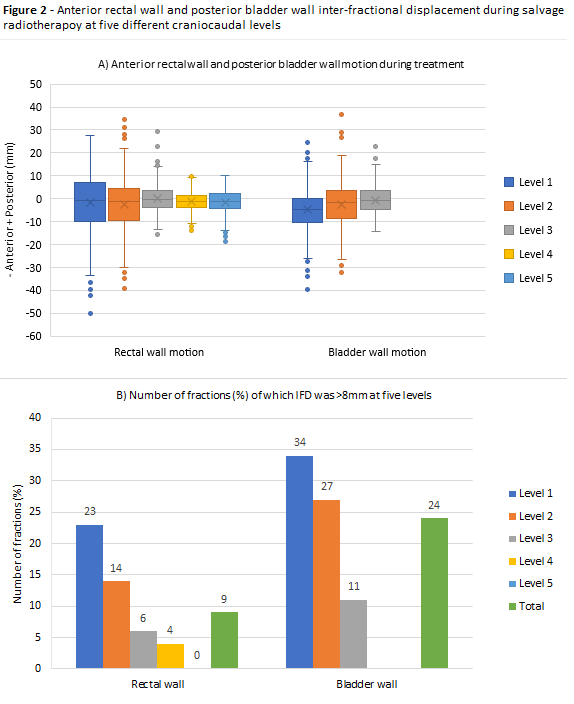
summarized in Figure 1. IFD >8 mm was correlated with change in rectal and bladder
volume during treatment (Mann-Whitney U: p<0.001 and p=0.008, respectively).
In 9 patients (75%), rectal wall IFD was <8 mm in >90% of fractions. In 5
patients (41%), bladder wall IFD was <8 mm in >90% of fractions. Patients with IFD of >8 mm showed large rectal or bladder volume
during planning-CT, with a median of 185.4 cm3 (IQR 154.8 to 236.5 cm3)
and 350.5 cm3 (IQR 225.9 to 402.1 cm3), respectively. The
largest IFD was seen at level 5, the most superior level (rectal wall IFD > 8mm
in 22% and bladder in 22%) (Figure 2). At the three most inferior levels, the IFD was <8 mm in 98% of
fractions.
Conclusion
In post-prostatectomy
salvage radiotherapy, inter-fractional AP displacement of the inferior CTV was within
the PTV margin of 8 mm in 98% of fractions. However, a wide variation in rectal
and bladder volumes during treatment was observed. With a stricter rectum and
bladder preparation and image-guided SRT protocol, CTV under- and OAR overdosing
is expected to be avoided.