Refinement of treatment setup accuracy using stereotactic system for paediatric immobilization
Santiago Velázquez Miranda,
Spain
PO-1486
Abstract
Refinement of treatment setup accuracy using stereotactic system for paediatric immobilization
Authors: Santiago Velázquez1, José-Luis León-García1, Felipe-Arturo Derecho-Torres1, David Muñoz-Carmona2, Florencio-Javier Luis-Simón1
1Virgen del Rocío University Hospitals, Department of Medical Physics, Seville, Spain; 2Virgen del Rocío University Hospitals, Department of Radiotherapy, Seville, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The purpose of the study was to investigate if stereotactic
system for paediatric immobilization (SSPI) can decrease setup deviations.
Material and Methods
The last 7 paediatric patients treated with Elekta
Synergy S 6-MV LINAC at our institution have been treated with tumours in the
superior abdomen, lungs, head and neck, receiving 141 fractions of radiotherapy
with a novel SSPI, designed for patients up to 1.20 meters in height. The
device has custom deformers for the cradle, which achieve an excellent
adaptation to the child's body, thermoplastic mask and stereotactic references.
Therefore, we do not use classic clinical setup of in-room lasers and
skin/cradle marks placed at simulation. The patient position was evaluated with
CBCT registered to the planning CT. A total of 101 cone-beams were analysed. Averages,
systematic errors, standard deviations, and root mean square values of observed
setup error were calculated. Couch shifts were registered to obtain Kernel
coordinates.
SSPI incorporates a
smartphone holder which enhances the collaboration of the patient. Children's
experience at simulation is critical for the success of any radiation therapy
treatment. Seven technologists were surveyed to assess their high, medium high,
medium low, and low satisfaction with children's experience, indexing, positioning,
and learning curve of the system.
Results
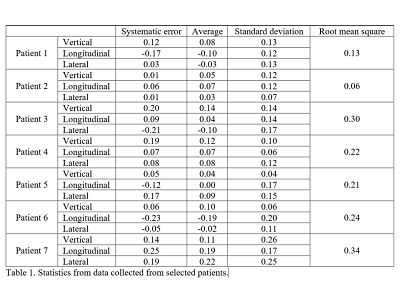
The mean translational displacement per patient, which
is the systematic displacement, ranged from x (-0.21 to 0.19 cm), y (-0.23 to
0.25 cm), z (-0.01 to 0.2 cm). Additionally, the SD of absolute random
displacement for individual patient ranged from x (0.07 to 0.25 cm), y (0.06 to
0.2 cm), z (0.07 to 0.25 cm) it sees figure 1 and table 1. For patients
receiving stereotactic treatment, 82.2% of those treatment sessions were within
our clinical tolerance of ≤ 3mm in any direction.
Technologists rated the children's experience
simulation, learning curve, set up, and positioning more highly for SSPI versus
classic clinical setup of skin/cradle marks.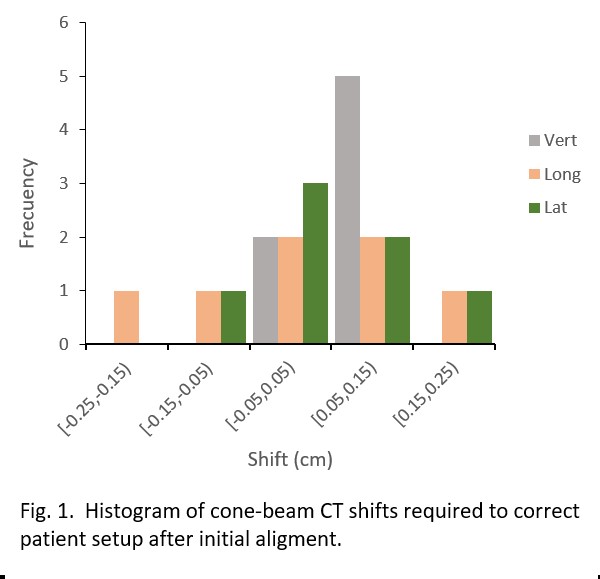
Conclusion
SSPI significantly improves localization of paediatric
tumours in comparison to classic setup of skin/cradle marks. This reduction in
the setup margin treated with SSPI could also have significant clinical
implications for second malignancies and acute and late radiation induced
toxicities.
Better results are
expected once the learning curve flattens. A larger prospective
trial is ongoing using a robotic couch for correcting setup errors in six
degrees of freedom.