SBRT in all-risk prostate cancer patients, first results from a chilean center with Halcyon linac
PO-1390
Abstract
SBRT in all-risk prostate cancer patients, first results from a chilean center with Halcyon linac
Authors: Hernan Letelier1, Gonzalo Rubio2, Yaniro Guillen1, Ruben Yañez1, Cristian Herrera1, Cristian Mendez1
1Hospital Clinico Regional de Valdivia, Radiation Oncology, Valdivia, Chile; 2IRAM Clinic, Radiation Oncology, Santiago, Chile
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is a well-validated treatment option in low- to favorable intermediate-risk (LR and FIR) localized prostate cancer (PC). Despite the growing prospective series in which the efficacy and safety of this technique have been described in unfavorable intermediate- to high-risk (UIR and HR) disease, this is not the standard and may be considered in patients with social or medical hardships.
Our radiotherapy (RT) public service receives patients from southern areas in Chile, including nearly 2.5 millions inhabitants in 1150 km of length. Adopting SBRT for broader indications when possible, such as PC, would help to expand access to curative RT.
Here, we present the first chilean series of SBRT in all-risk groups PC, using coplanar O-ring Halcyon Linac (Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA).
Material and Methods
Consecutive patients with cT1-3a N0M0 PC treated with SBRT between May 2019 and September 2021 were included in this prospective cohort. No restrictions were made regarding prostate volume or International Prostate Symptom Score.
A total dose of 36.25 Gy in 5 non-consecutive fractions was administered with volumetric modulated arc therapy. All treatments were calculated with Eclipse TPS and delivered in Halcyon Linac with single-energy 6MV-flattening filter free beam; model V1.0 equipped with MV-CBCT and model V2.0 with kV-CBCT. For low-risk PC, CTV= prostate; for intermediate-risk PC, CTV= prostate + 1 cm seminal vesicles (SM); for high-risk PC, prostate + 2 cm SM. PTV= CTV + 3-5mm.
We register clinical variables, dosimetric results and acute toxicities using RTOG score. In those results, a comparison between LR-FIR and UIR-HR was made.
Results
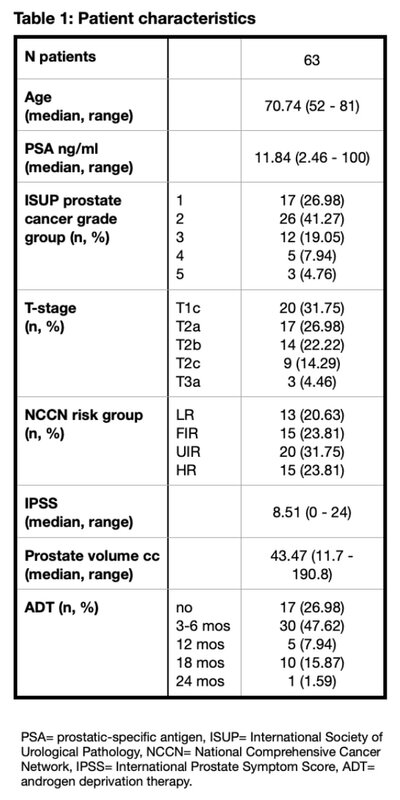
Sixty-three patients were included in this review, with a median age of 70.7 years (range: 52-81). According NCCN risk classification, 35 patients (55.56%) were UIR or HR disease. (Table 1)
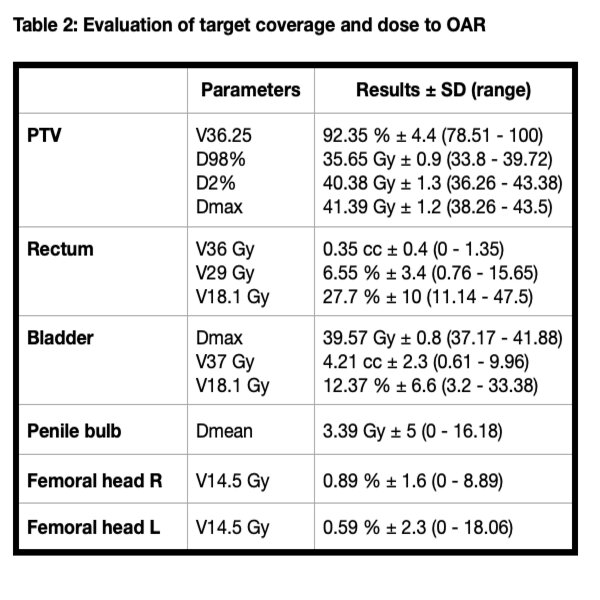
Forty-six patients (73%) received androgen deprivation therapy, mostly (30) between 3-6 months. SBRT was completed in 11 days (median, range: 9-28). All plans accomplished with organ of risk constraints (Table 2). No acute toxicity grade ≥3 was described, with gastrointestinal (GI) G1 14.29% and G2 6.35% and genitourinary (GU) G1 33.33% and G2 28.57%. No significant differences were noted between LR-FIR and UIR-HR (p=0.57 for GU and p=0.81 for GI>.05).
Conclusion
Despite long-term results are awaited, implementation of SBRT in patients with localized PC in more unfavorable risk groups is feasible, achieving a favorable toxicity profile and adequate dose distribution to target volumes and OAR with Halcyon Linac. This technique improve compliance and access to treatment in our population with social disparities.