SBRT in prostate cancer: annalysis of CBCT guided radiotherapy and on-line correction
PO-1381
Abstract
SBRT in prostate cancer: annalysis of CBCT guided radiotherapy and on-line correction
Authors: Jorge Olivares1, Jose Solis Campos2,1, Gabriel Lazcano Alvarez1, Gabriel Veillon Contreras2,1, Benjamin Tudela Staub2,1, Ilan Perrot Rosenberg1
1Universidad de Valparaiso, Oncology, Valparaiso, Chile; 2Carlos Van Buren Hospital, Oncology, Valparaiso, Chile
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) precisely delivers a high radiation dose towards an extracranial target in 1 to 5 fractions. The purpose of this study is to describe the treatment characteristics and acute toxicity in a cohort composed of prostate cancer patients treated with CBCT guided SBRT without fiducial markers.
Material and Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of patients treated with SBRT between 2020 – 2021 at Carlos Van Buren Hospital in Valparaíso with a flattening filter free volumetric modulated arc therapy. CTV was defined as: 1) Prostate (low risk patients) 2) Prostate + 1 cm Seminal Vesicles (S.V) (intermediate risk) 3) Prostate + 2 cm S.V. PTV = CTV +0.5 cm (0.3 cm posteriorly). Prescription consisted of 36.25 Gy in 5 fractions (alternate days) to Prostate PTV and 27.25 Gy in 5 fractions to S.V PTV. On-line correction was performed before each session. Patients were treated in a Elekta, Versa HD. Acute toxicity was registered according to the RTOG definition (<90 days since treatment end). The study was approved by the ethics committee.
Results
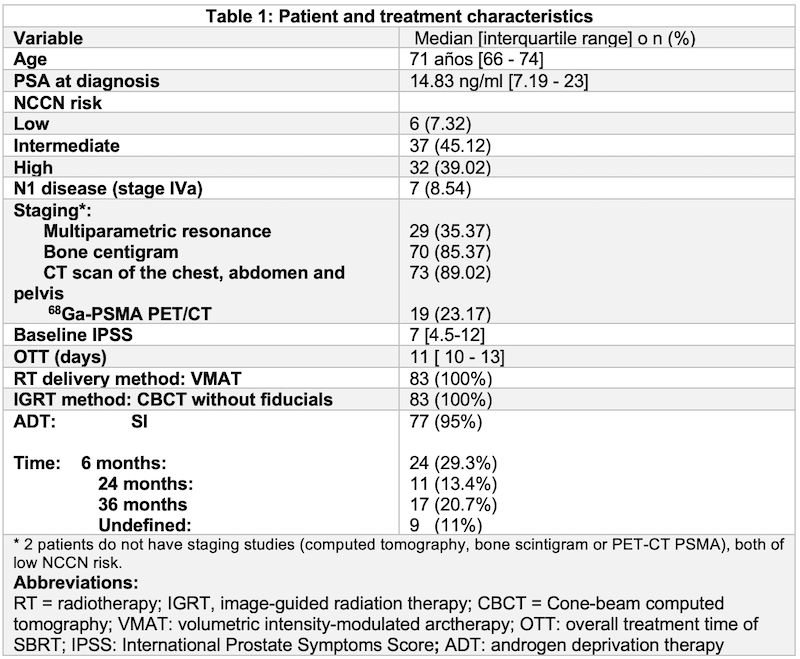
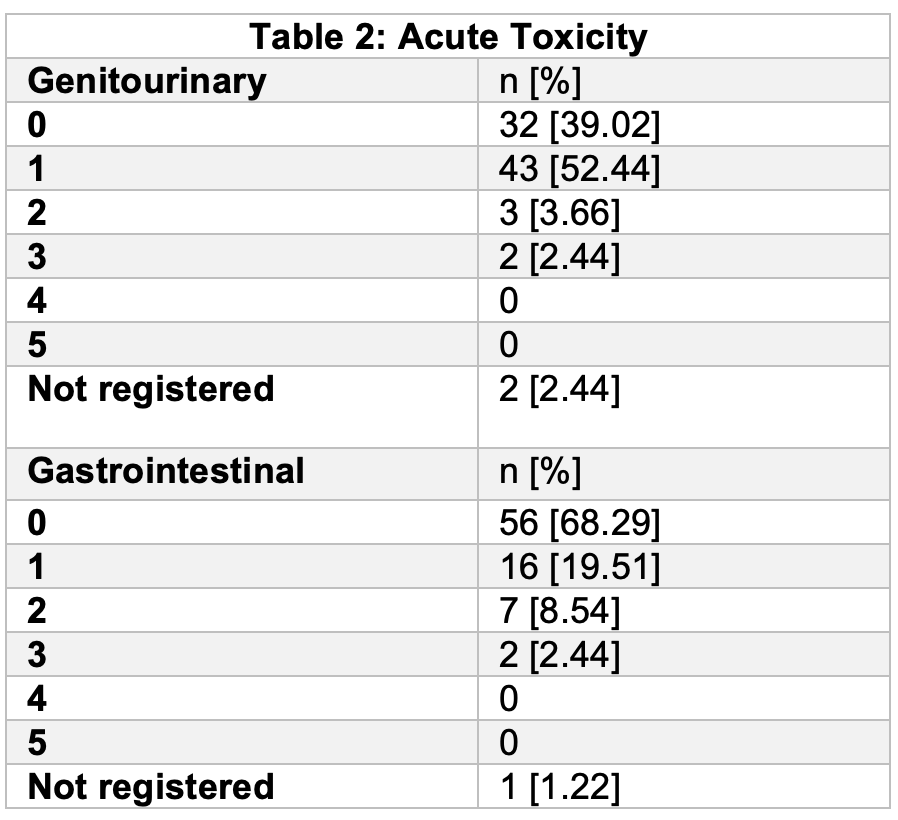
82 patients were included. Median PSA was 14.83 (IQR 7.19-23). 32 (39.02 %) patients had high risk disease. In 62 (77.5%) patients radiotherapy planning was done based on MRI / CT fusion. Median treatment delivery time (Beam On Time) was 139.7 s. 71.3% of patients suffered some form of acute toxicity; 2 patients G3 acute gastrointestinal toxicity and 2 patients G3 acute genitourinary toxicity, no G4-G5 toxicity was observed. Only 1 patient had to discontinue treatment due to acute urinary obstruction caused by disease progression.
Conclusion
CBCT guided SBRT and online correction allows a safe target and organ at risk monitorization, permitting a high dose delivery with an excellent acute toxicity profile. Efficacy results will be reported once appropriate follow up is reached.