IORT for Brain Metastases: Final First-Stage Results of a Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial
PO-1145
Abstract
IORT for Brain Metastases: Final First-Stage Results of a Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial
Authors: Douglas Castro1, Paulo Sanematsu Jr.2, Antônio Cássio Pellizzon1, Sérgio Suzuki2, Ricardo Fogaroli1, José Eduardo Dias Jr.2, Guilherme Gondim1, Daniel Estrada2, Maria Letícia Silva1, Márcio Rassi2, Michael Chen1, Richard Giacomelli2, Henderson Ramos1, Elson Neto1, Carolina Abrahão1, Tharcisio Coelho1, Liao Yu3, Cássio Tannous1, Vinicius Calsavara4, Frank Giordano5, Jean Oliveira2
1A. C. Camargo Cancer Center, Radiation Oncology, São Paulo, Brazil; 2A. C. Camargo Cancer Center, Neurosurgery, São Paulo, Brazil; 3A. C. Camargo Cancer Center, Imaging, São Paulo, Brazil; 4A. C. Camargo Cancer Center, Statistics and Epidemiology, São Paulo, Brazil; 5University Hospital Bonn, Radiation Oncology, Bonn, Germany
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Focal stereotactic radiosurgery to the surgical
cavity lowers local recurrence after resection of brain metastases (BM). We did
this study to evaluate local control (LC) and brain disease control (BDC) after
intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) for completely resected BM.
Material and Methods
In this investigator-initiated,
single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial, adult patients (aged 18 years or older)
with one completely resected supratentorial BM in the presence of up to 10
lesions suggestive of BM were recruited. All patients were treated with 50 kV portable linear accelerator using
spherical applicators into the surgical cavity with a prescribed dose of 18 Gy
to a depth of 1 mm. The primary endpoints were actuarial LC and BDC (LC
associated with the absence of new distant BM). Local failure (LF) and distant
brain failure (DBF), with death as a competing risk, were estimated. Secondary
endpoints were overall survival (OS) and incidence of radiation necrosis (RN).
A Simon two-stage design was used and estimated an accrual of 10 patients for
the first-stage analysis and a LC higher than 63% to proceed to the second
stage. We report the final analysis of the first stage after a minimum follow-up
(FU) of 6 months was completed for all alive patients. Data set was locked on
June 15, 2021. This
trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT03789149.
Results
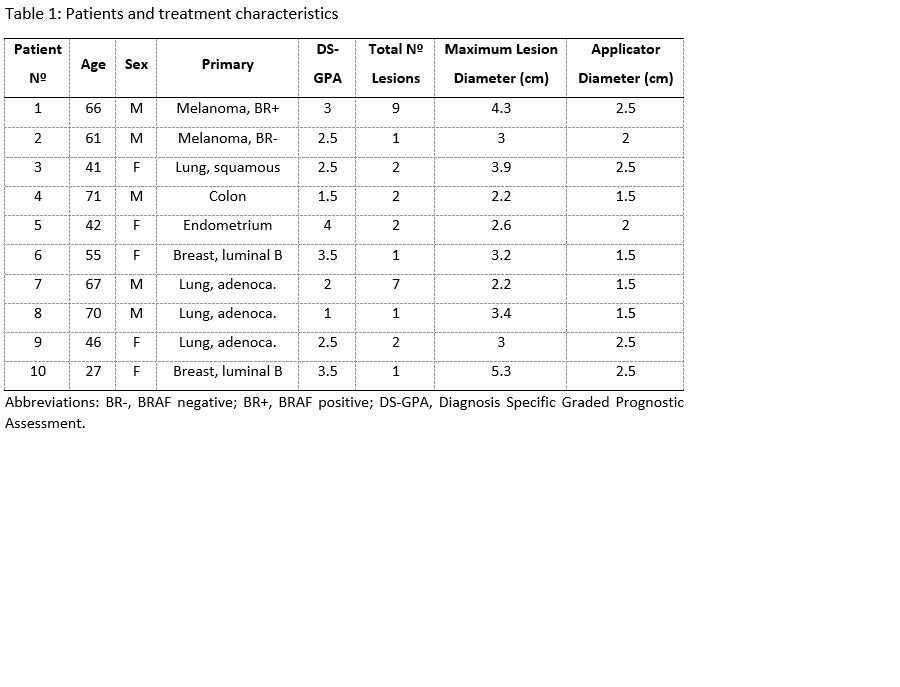
Between June 11, 2019, to November 17, 2020, 10
patients were accrued. The primary tumors were lung cancer in four patients,
breast cancer and melanoma, each in two patients, and colon and endometrial
cancer, each in one patient (Table 1). The median clinical and imaging FU was
11.2 (IQR 8.2-22.7) and 9.7 (ICR 6.0-14.3) months, respectively. One patient
had local failure 3 months after IORT and three patients died due to
extracranial progression during the FU period. Median LC was not reached and median
BDC was 5 months (95% CI 2.37-7.62). The 6-month and 12-month LC was 87.5%. The
6-month and 12-month BDC was 39% and 13%, respectively. The incidence of LF at
6 and 12 months, with death as a competing risk, was 10%. The incidence of DBF
at 6 and 12 months, with death as a competing risk, was 50% and 70%,
respectively. All patients who developed DBF were salvaged with focal
stereotactic radiotherapy during the FU time, with no failure with
leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Median OS was not reached. The 6-month and
12-month OS was 80%. One patient had asymptomatic RN 10 months after IORT.
There were no patients with wound dehiscence.
Conclusion
IORT
for completely resected BM is associated with a promising high local control
and low risk of RN, reaching the pre-specified criteria to proceed to the
second stage and warranting further studies.