Large intra-fractional tumor position variations in deep-inspiration breath-hold lung SBRT
Wiviann Ottosson,
Denmark
PD-0232
Abstract
Large intra-fractional tumor position variations in deep-inspiration breath-hold lung SBRT
Authors: Wiviann Ottosson1, Niels C Rand Momsen1, Sarah Fortin Jørgensen1, Susanne N Bekke1, Patrik Sibolt1, Claus P Behrens1, Gitte Fredberg Persson1
1Copenhagen University Hospital – Herlev and Gentofte, Department of Oncology, Copenhagen, Denmark
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Deep-inspiration breath-hold
(DIBH) stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is an option for very mobile or
very small lung tumors. Inter-fractional tumor position variation is minimized
by daily cone-beam CT (CBCT), but the extent of intra-fractional tumor position
variation is difficult to assess.
The aim of this study
was to estimate the intra-fractional tumor position variation based on CBCTs acquired
before and mid-treatment for patients receiving lung SBRT in DIBH and free
breathing (FB). Additionally, investigate what impact two different patient
cohorts have on the resulting setup margins.
Material and Methods
Two patient cohorts (MM1
(from April 2018 to March 2019), and MM2 (from October 2020 to September 2021)),
in total 84 consecutive patients scheduled for lung SBRT (67.5 Gy / 3 fractions,
45 Gy / 3 fractions, or 50 Gy / 5 fractions) were retrospectively included in
this study. Both cohorts included 21 DIBH and 21 FB patients each. Patients
were selected for DIBH treatment if peak-to-peak tumor motion in the
longitudinal (LNG) direction exceeded 1 cm in FB. The patients were
audio-visually guided during DIBH, to a comfortable patient-specific breath-hold
level using a gating window of 2–3 mm. Both cohorts used a marker based optical
tracking system at treatment (Respiratory gating for TrueBeam, Varian). Pre-
and mid-treatment CBCT were acquired for all fractions to evaluate the
intra-fractional tumor position variation. All CBCTs were registered to the planning
CT by soft-tissue tumor match. Resulting offsets were used to calculate
bi-directional setup margins based on van Herk formalism for lung (van Herk et
al. 2000). The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for statistical testing regarding
differences in tumor position variation between FB and DIBH, and between the
two patient cohorts. The results were considered statistically significant for
p < 0.05.
Results
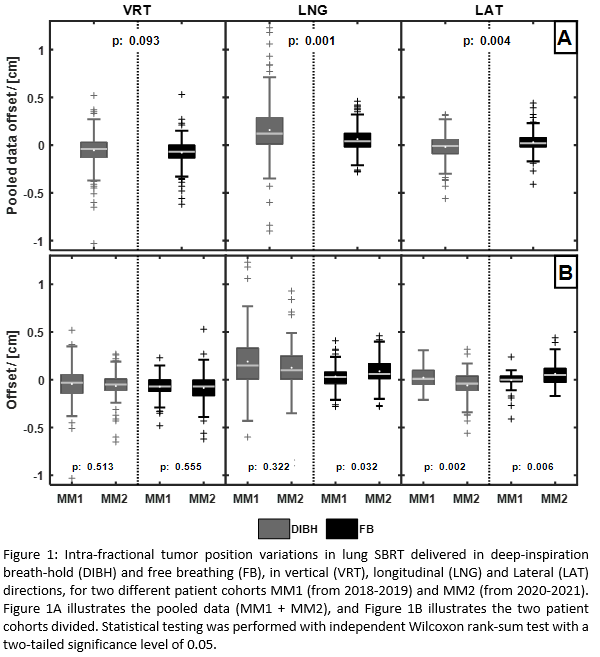
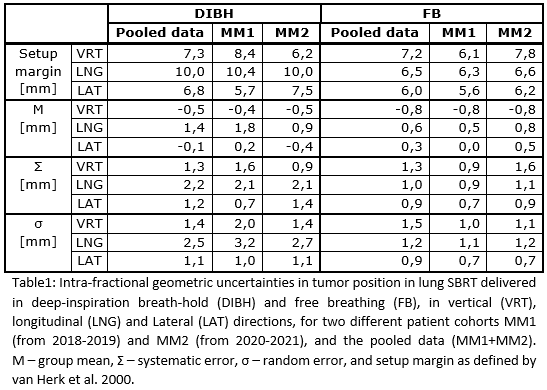
A statistically significantly
larger intra-fractional tumor position variation in LNG was observed for DIBH
compared to FB for the pooled data (MM1+MM2, Figure 1A) (p = 0.001), resulting
in a 3-4 mm larger setup margin (Table 1). In the lateral (LAT) direction the
observed difference was small, but statistically significant (p = 0.004) and
resulted in setup margin being 1 mm larger in DIBH compared to FB. No statistically
significant difference in intra-fractional tumor position variation was
observed in the vertical (VRT) direction and the resulting setup margins were
identical for FB and DIBH respectively. Variations between MM1 and MM2 were in
general small. Calculating setup margins based on the pooled data were found to
be clinically acceptable, within approximately 1 mm differences (Table 1).
Conclusion
Large intra-fractional tumor position variations during DIBH SBRT for
patients with tumors moving > 1cm in FB result in increased setup margins
compared to FB SBRT for patients with tumors moving < 1cm. Pooling data from
two patient cohorts were clinically acceptable.