Differences between HPV positive and negative oropharyngeal cancer detected by Non-Gaussian IVIM
Nienke Sijtsema,
The Netherlands
OC-0625
Abstract
Differences between HPV positive and negative oropharyngeal cancer detected by Non-Gaussian IVIM
Authors: Nienke Sijtsema1,2, Iris Lauwers1, Gerda Verduijn1, Dirk Poot2, Aad van der Lugt2, Juan Hernandez-Tamames2, Mischa Hoogeman1,3, Steven Petit1
1Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Department of Radiotherapy, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 2Erasmus MC, Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 3HollandPTC, Department of Medical Physics and Informatics, Delft, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of diffusion
weighted imaging (DWI) has been associated with response to treatment for oropharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC). However, recently it has been suggested that
ADC value is a surrogate of human papillomavirus (HPV) status, and not an
independent prognostic factor. Non-Gaussian Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (NG-IVIM) imaging is a novel extension of conventional DWI that enables simultaneous
assessment of microvascular perfusion and inter- and intra-cellular diffusion. This
provides a more detailed picture of the tumor micro-environment than ADC only. Recently,
we optimized NG-IVIM specifically for the head-and-neck region in volunteers. Here,
for the first time, the optimized acquisition was applied in OPSCC patients. The
aim of this study is to investigate the differences in NG-IVIM parameters between
HPV positive (HPV+) and HPV negative (HPV-) OPSCC and compare NG-IVIM parameters
to the ADC derived from conventional DWI.
Material and Methods
Thirty-one consecutive OPSCC patients that underwent a
planning MRI including a DWI scan (b=0, 10, 2x80, 130, 570, 2x770, 2x780, 790 and 4x1500 s/mm2) between February 2020 and September 2021
were included. The DWI images were corrected for geometric distortion and
rigidly registered to the T2w images acquired during the same scan session. With
help of T1w images with and without gadolinium contrast, the GTV was segmented
on the T2w images by an experienced radiation oncologist, and projected on the
DWI. Within the GTV, voxel-wise fitting of the conventional mono-exponential
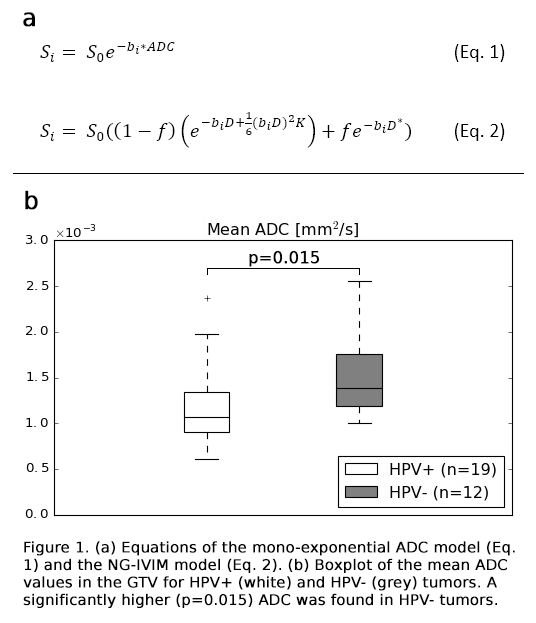
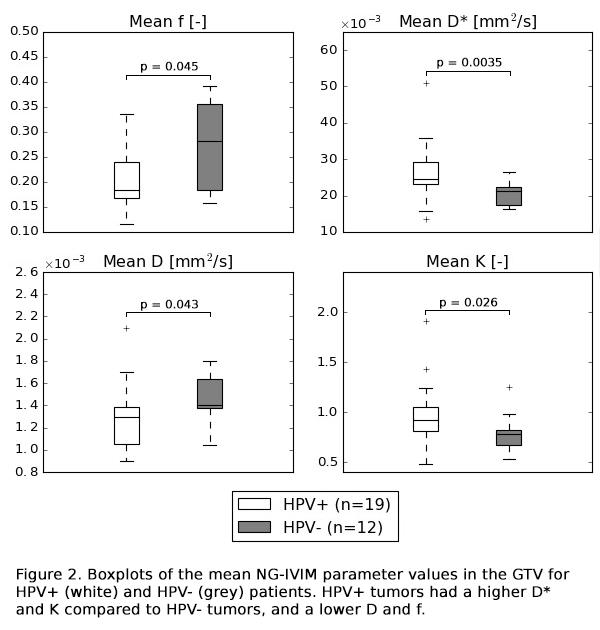
ADC model and the bi-exponential NG-IVIM model (Figure 1a) was performed, and ADC, the free
diffusion coefficient D, pseudo-diffusion coefficient D*, perfusion fraction f, and kurtosis K were estimated. D* and f are both
related to microvascular perfusion, while K is related to restricted diffusion
and cellularity. The average D,
K, f and D*, and ADC were compared between HPV+ and HPV- tumors using
a Wilcoxon rank sum test. A p-value<0.05 was considered statistically
significant.
Results
In
total 19 HPV+ and 12 HPV- tumors were included. The rank sum test revealed a
significantly lower (p=0.015) ADC in HPV+ compared to HPV- tumors, in line with
literature (Figure 1b). Moreover, aside
from a significant difference in D
(p=0.043), also differences in the perfusion related parameters f (p=0.045) and D* (p=0.0035) and the cellularity related parameter K (p=0.026) were found (Figure 2).
Additionally, the range of ADC is larger than the range of D, indicating a
contribution of microvascular perfusion in the ADC that is not accounted for in
the mono-exponential model.
Conclusion
NG-IVIM revealed differences in both microvasculature
and cellularity between HPV+ and HPV- tumors, in addition to the difference in
ADC obtained from conventional DWI. So, NG-IVIM is capable of providing
a much more detailed picture of the tumor micro-environment and could aid in
the understanding of differences between HPV+ and HPV- tumors.