Dosimetric and clinical aspects of lung SABR delivered with Synchrony® tracking on Tomotherapy
PD-0982
Abstract
Dosimetric and clinical aspects of lung SABR delivered with Synchrony® tracking on Tomotherapy
Authors: Marzia Cerrato1, Elena Gallio2, Fabio Menegatti1, Ilaria Bonavero1, Cristiano Grossi1, Chiara Casale1, Paolo Brossa3, Serena Badellino1, Francesca Romana Giglioli2, Ramona Parise1, Mario Levis1, Umberto Ricardi1
1University of Turin, Department of Oncology, Turin, Italy; 2A.O.U. Città della Salute e della Scienza, Medical Physics Unit, Turin, Italy; 3A.O.U. Città della Salute e della Scienza, RTT Member, Turin, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
In 2020 Synchrony® was installed on Radixact® tomotherapy at our department. This study compares the Radixact® plans and the LINAC-based lung SABR plans to evaluate possible SABR-induced toxicities resulting from the two different techniques.
Material and Methods
Patients with early-stage NSCLC or oligometastatic lung tumors, PS ECOG 0-1, with a single nodule, in peripheral location were included. All patients completed the simulation phase successfully and were treated with the Synchrony® plan conforming to a “risk adapted” fractionation schedule (3-5 fractions). A LINAC-based plan was prepared for back-up. A dosimetric comparison was made between Radixact® tomotherapy and LINAC-based plans (Elekta® Versa HD). Beam-on time (BOT), PTV parameters (volume, volume at the prescribed dose, mean dose, and conformity number index), EQD2Gy mean dose (Ipsilateral lung – PTV), and volume (%) at different dose levels for (Lungs-PTV) and (Ipsilateral lung – PTV) (V5Gy, V10Gy, V13Gy, V15Gy, V20Gy and V25Gy) were considered. The volume of the isodose of 10 Gy, 15 Gy, 18 Gy, 20 Gy, and 30 Gy were also compared. Radiological toxicity was evaluated according to the Ronden et al classification of lung SABR outcomes. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was applied for all parameters and a level of significance of 5% was considered.
Results
From July 2020 to July 2022, 18 patients were enrolled. The median beam-on time (BOT) for each fraction was 9.3 minutes (IQ range: 8.6-10.5). The following dose-volume parameters were statistically different between the two plans: BOT, (p<0.001), PTV volume (p<0.001), conformity number index (p=0.04), and volume of 15 Gy (p=0.002), 18 Gy (p<0.001), 20 (p<0.001) and 30 Gy (p=0.02) isodoses (Figure 1). With a median follow up of 15 months, approximately 67% of patients displayed radiological toxicity, mostly asymptomatic or with mild symptoms: 5 diffuse consolidations, 4 diffuse Ground Glass Opacities (GGOs), 3 patchy GGOs, 16 late scar-like fibrosis, 1 late mass like-fibrosis. These radiological outcomes have different features and a faster onset than in patients treated with LINAC-based plans, which have been employed extensively at our institute.
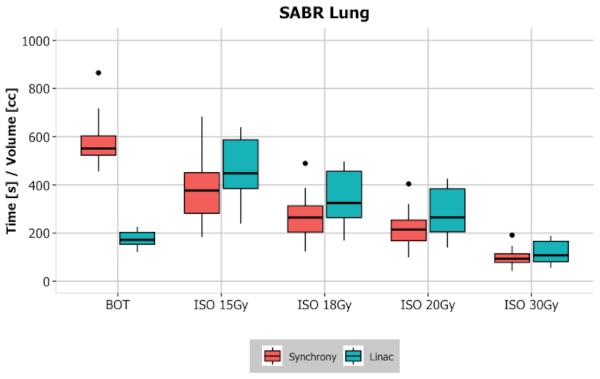
Conclusion
LINAC-based lung SABR gives rise to a variety of toxicities that are strongly dependent on both patient-related factors and planning/dosimetry-related factors. There are no studies investigating the toxicity of lung SABR with Synchrony® tracking on Radixact® Tomotherapy. Preliminary data highlight a statistically significant difference in terms of volumes of isodose and suggest a possible correlation between these volume parameters and the development of SABR-related radiological toxicity. No differences in terms of clinical toxicity were found between patients treated with the two techniques. Further studies including a larger number of patients and longer follow-ups are necessary to draw more robust conclusions.