1. It was found that in addition to IL-10, COX-2, TLRs, FOXP3, PD-1, PD-L1, EGFR, MAPK, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF, and IL-17a molecules increased during VMAT compared with baseline through the determination of inflammatory factor proteins in peripheral blood, among which the secretion of COX-2, TLRs, IL-2 and IL-6 were time/dose dependent.
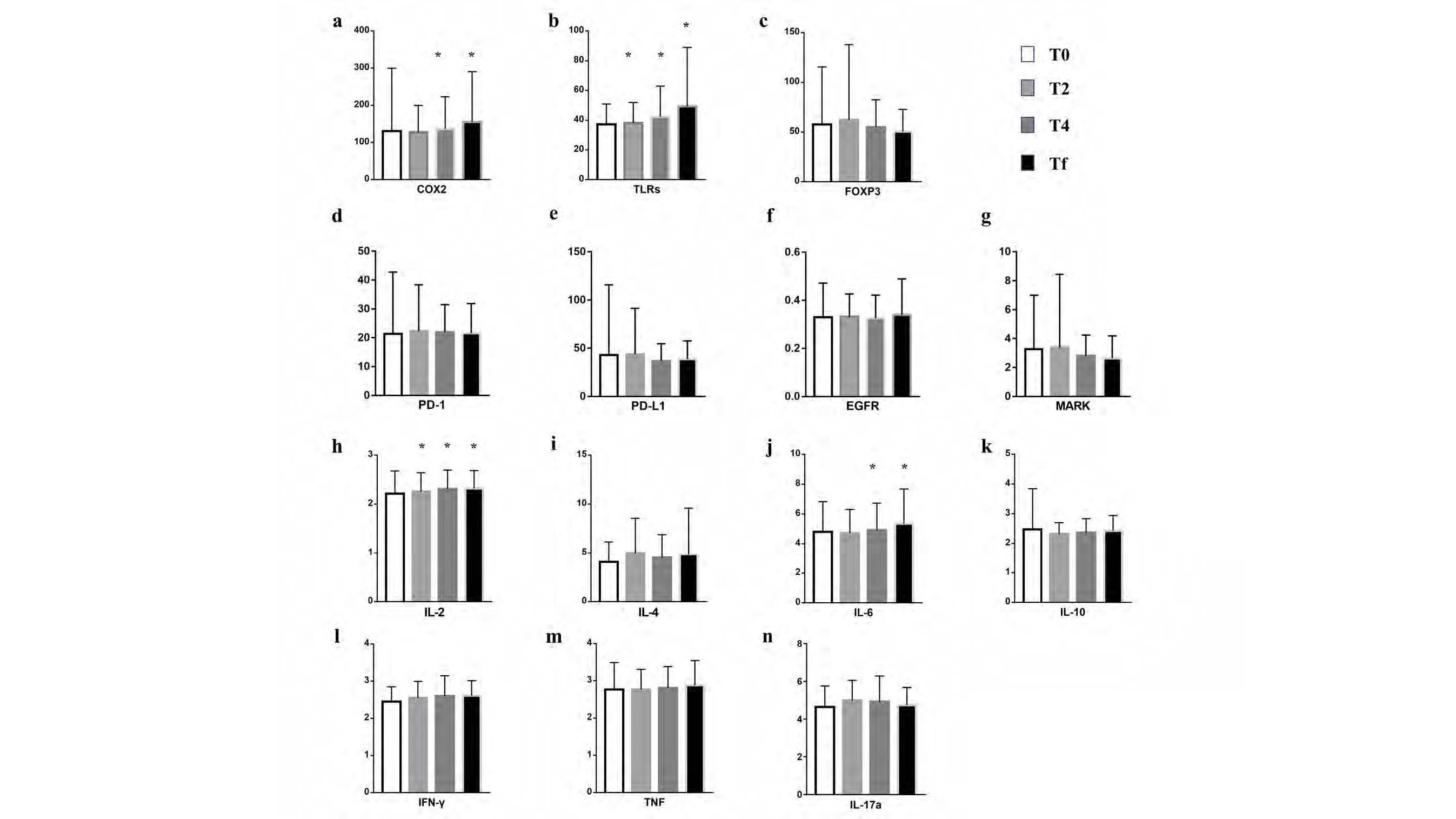
2. Through ROC curve analysis, it was found that IL-6 could be used as an inflammatory molecule to predict RE, and IL-6 and COX-2 could be used as inflammatory molecules to predict SARE. The inflammatory factors of RE and SARE were preliminarily identified.
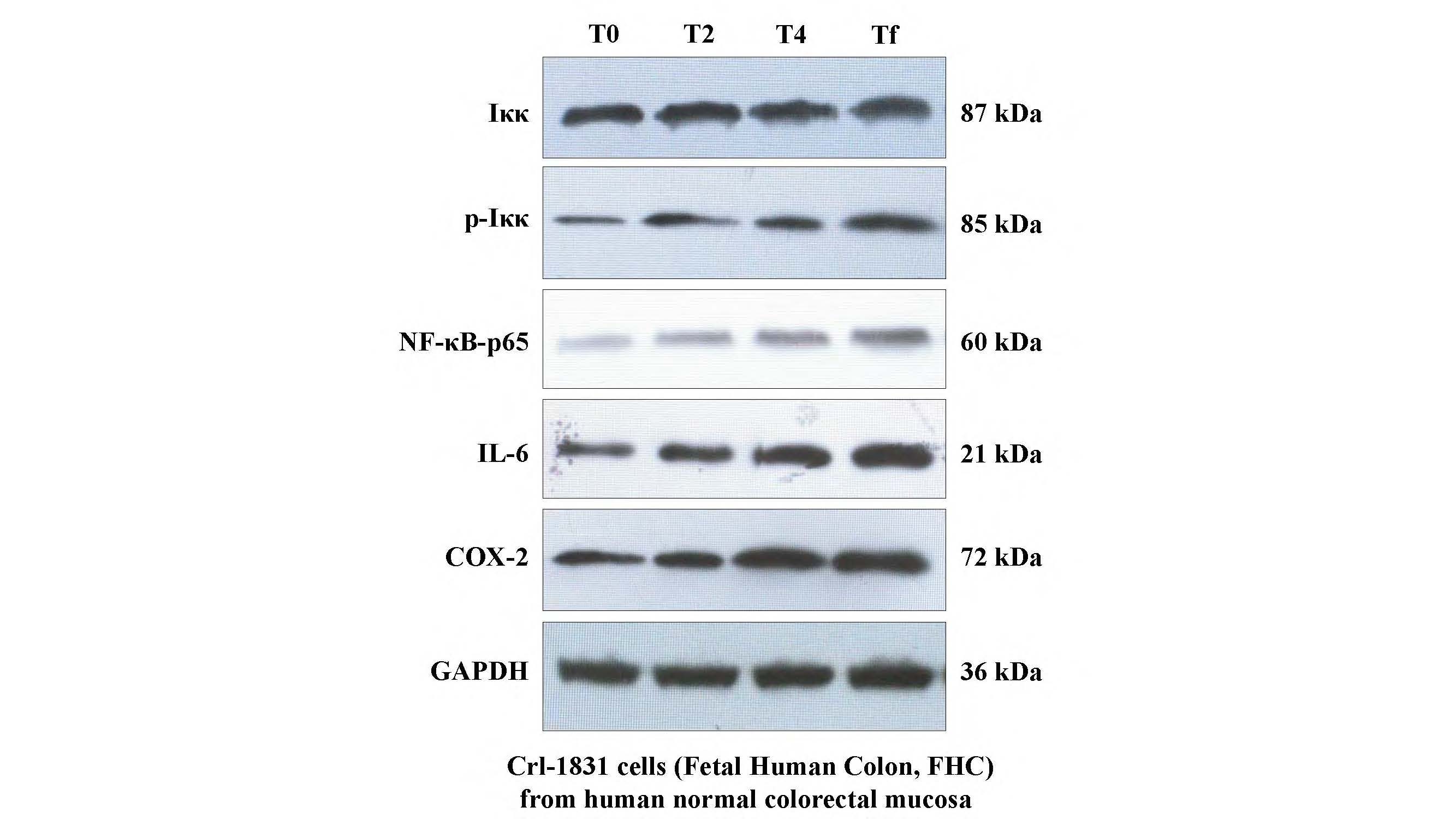
3. The supernatant and cell lysate which were co-cultured with the fecal suspension from cervical cancer patients during VMAT and FHC were collected for total protein extraction. The protein expressions of p-Iκκ, NF-κB-p65, IL-6 and COX-2 were found to be time/dose dependent. Moreover, the phosphorylation of Iκκβ at Ser176 and Ser177 up-regulated the expression of NF-κB-p65, IL-6 and COX-2 downstream of the pathway.