A Pilot Initiative Using Telemedicine in Online Reviewing of CBCT For Stereotactic Radiation Therapy
Yuen Nee Yvonne LOH,
Singapore
PO-2309
Abstract
A Pilot Initiative Using Telemedicine in Online Reviewing of CBCT For Stereotactic Radiation Therapy
Authors: Yuen Nee Yvonne LOH1
1National University Cancer Instituite Singapore, National University Health System, Radiation Oncology, Singapore, Singapore
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
On-site to review and approval of the cone-beam computed tomography prior to the radiation delivery has been the usual practice. Remote review using telemedicine1,2 was formulated to reduce waiting time and travel time. The COVID-19 pandemic made on-site review increasingly challenging due to team segregation and movement cessation between hospitals had to be imposed. A pilot study was conducted to quantify the benefits of using telemedicine for online reviewing and approval of cone-beam computed tomography prior to stereotactic ablative radiation therapy delivery from March 2020 to December 2021. 74.9 % of the patients (212 out of 283) receiving stereotactic radiation therapy benefited from this new initiative.
The aim of the study is to quantify the realized time savings and utilization of appointment slots for patients.
Material and Methods
- Baseline data of patients received stereotactic body radiation therapy, stereotactic fractionated radiation therapy to brain and stereotactic radiosurgery to brain were obtained.
- Consensus among the radiation oncologists for the initiative
- Explore the options of secured network, speed of network, suitable mobile devices and its immobilization gear to allow better viewing of cone-beam computed tomography
- Establish the workflow and work process especially radiation oncologists stationed off-site
- Reduce time spent for patients in the department
- Reduce time wastage for radiation oncologists to travel between hospitals
- Improve appointment allocation for patients
- Increase radiation oncologists’ consultation slots
- Improve radiation oncologists’ job satisfaction
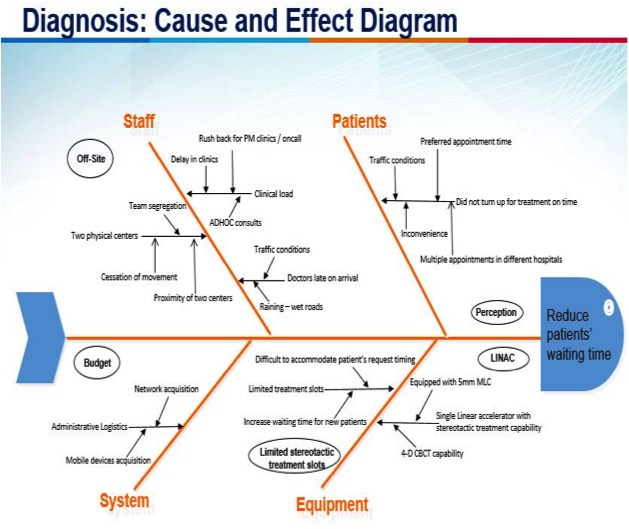
Results
There are 162 out 168 patients receiving stereotactic radiation therapy to the body, 50 out of 97 receiving stereotactic radiation therapy to the brain trial under the initiative. Baseline data was collected and patients often spend an average of 60 minutes in the department on the day of their treatment. The median time patient spent was reduced to 45 minutes. Prior the intervention, radiation oncologists have to travel between hospitals and be on-site to view and approve the cone-beam computed tomography and often delay at the other centre’s clinics, weather, road conditions are causes of the delay to be on-site. Intervention to improve workflow was implemented with the introduction of using telemedicine for viewing and approval of cone-beam computed tomography.
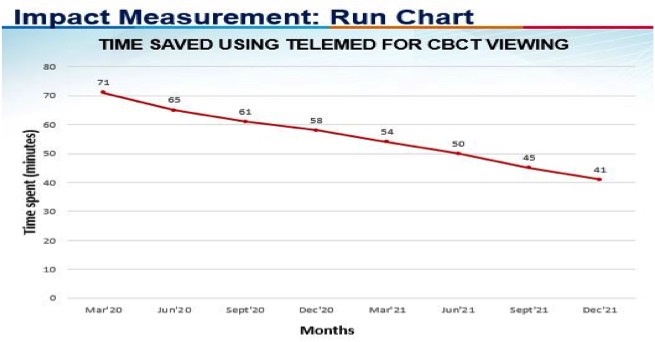
Conclusion
- Minimize time spent in hospital for patients
- Maximize appointment slots allocation for stereotactic treatment
- Reduce time wastage for radiation oncologists travel between hospitals
- Increase patients’ satisfaction3
- Increase radiation oncologists’ consultation slots- The modified work process has managed to reduce the time spent for patients during their day of radiation therapy and time saving for staff with improved utilization and allocation of appointment slots. We have continue to monitor and discussions for ongoing strategies to ensure sustainability.