Characterization of a novel detector array for daily quality assurance in proton therapy
Henry-Aravinth Devendranath,
Germany
PO-1699
Abstract
Characterization of a novel detector array for daily quality assurance in proton therapy
Authors: Henry-Aravinth Devendranath1, Veronika Flatten2, Ndimofor Chofor3, Jörg Wulff4, Beate Timmermann5, Andreas A. Schönfeld3
1Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Medical Physics, Düsseldorf, Germany; 2Marburger Ionenstrahl-Therapiezentrum, Medical Physics, Marburg, Germany; 3Sun Nuclear, A Mirion Medical Company, Research, Melbourne, USA; 4Westdeutsches Protonentherapiezentrum Essen, Medical Physics, Essen, Germany; 5Westdeutsches Protonentherapiezentrum Essen, Proton therapy, Essen, Germany
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The aim of this project was to characterize and verify a prototype detector array for daily quality assurance (QA) in proton therapy according to TG 224. A fast array calibration method and corresponding QA dose maps were tested and evaluated.
Material and Methods
The prototype array is designed to verify the spot position and size, as well as the energy range of proton pencil beams in daily routine quality assurance. This is achieved by a unique layout of air-filled ionization chambers: a central chamber surrounded by four others. The array is composed of 25 chambers, which are grouped in five clusters, each associated with different build-up depths.
The calibration method, as well as the sensitivity and accuracy of the calibrated array towards changes in the aforementioned beam parameters was investigated on several active scanning proton beam lines.
Results
The array was able to reliably detect and characterize the changes in the spot shift, spot size and energy, while the calibration method takes less than 7 minutes and accounts for beam line variations of the pencil beam characteristics, as well as response variations of the individual chambers. The delivery of the complete QA dose map, which is used on daily bases, takes less than one minute. Figure 1 shows the array’s response parameters towards x- and y-shifts and spot size changes of the beam (top panels), as well as towards energy range changes of the beam (bottom panel) for one example beam line.
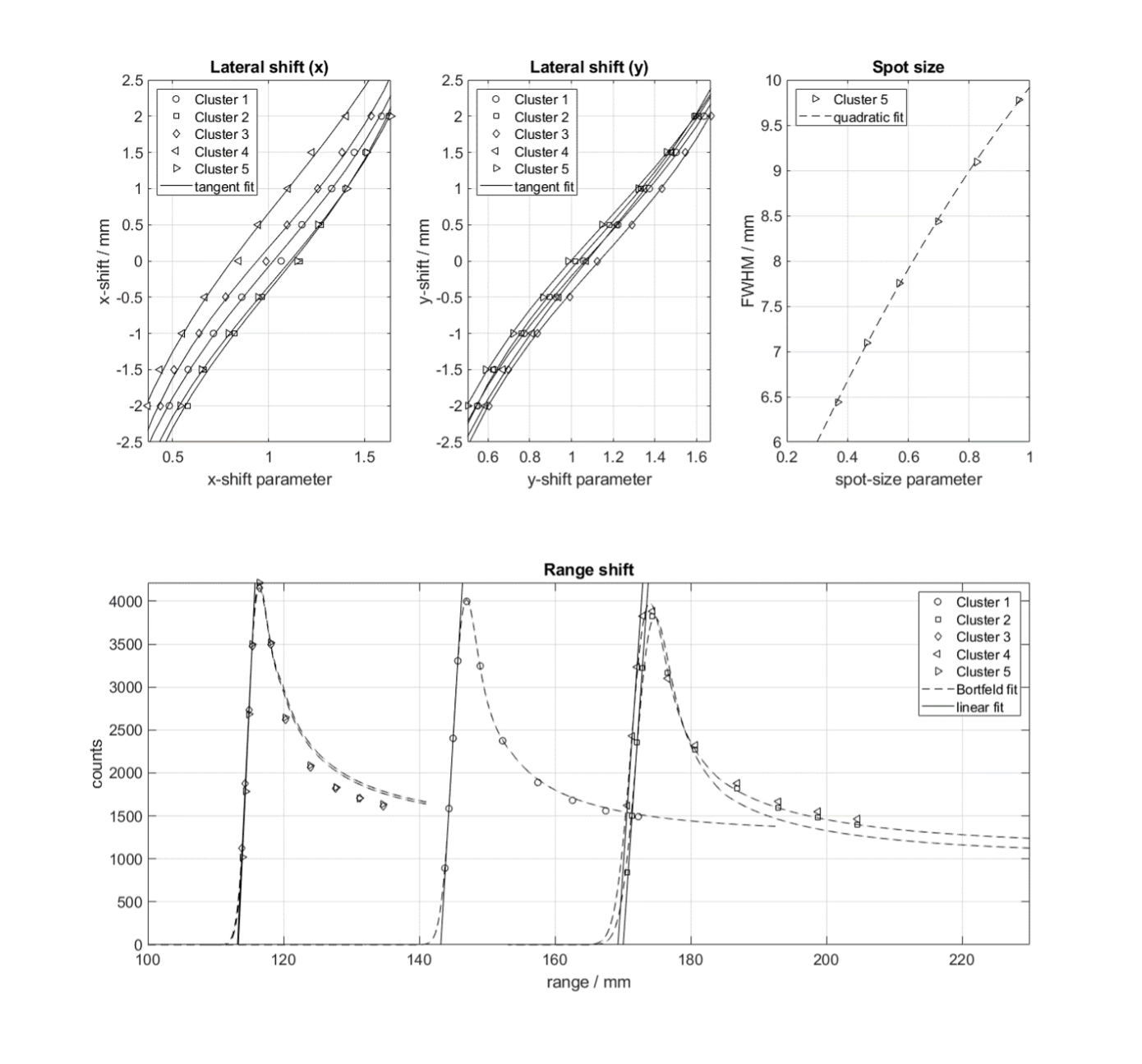 Figure 1: Top panels show the sensitivity of the QA parameter towards beam shifts in x- and y-directions, as well as to variations of the beam spot size, each measured at an energy of 226.7 MeV. The sensitivity towards energy range changes is characterized by the distal slopes, shown here as linear fits (bottom panel).
Figure 1: Top panels show the sensitivity of the QA parameter towards beam shifts in x- and y-directions, as well as to variations of the beam spot size, each measured at an energy of 226.7 MeV. The sensitivity towards energy range changes is characterized by the distal slopes, shown here as linear fits (bottom panel).
Conclusion
The prototype array offers a fast way to determine and track the spot position, spot size and energy range of the beam in daily QA measurements.