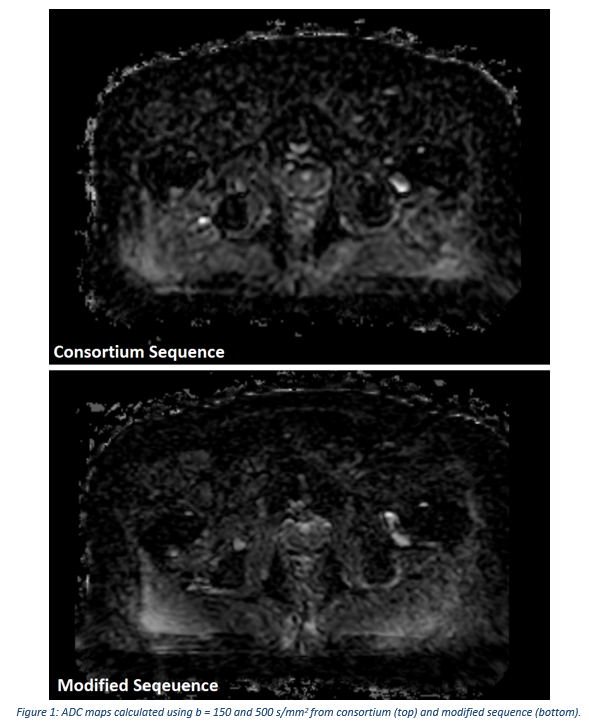
The consortium sequence (SS-EPI DWI, b = 0, 150, 500 s/mm2 (2, 4, 16 averages respectively), TE/TR = 82/3354 ms, voxel = 1.9x1.9x4.0 mm, Averages = 1, TA = 3:31) was modified to improve in-plane resolution and increase SNR (SS-EPI DWI, b = 150, 500 s/mm2 (5, 12 averages respectively), TE/TR = 70/2800 ms, voxel = 1.4x1.4x5.0 mm2, Averages = 2, TA = 4:48). The b = 0 image was removed as it is not used to calculate the ADC map. Additional averages were added to the b = 150 and 500 s/mm2 images to improve SNR.
Thirteen patients treated on the MRL, recruited to the MOMENTUM study, were scanned with both sequences at their MR planning session.
Visual image quality assessment of the DWI images and ADC maps was undertaken by a radiologist who assessed the appearance of the whole prostate, transitional/peripheral zones (TZ/PZ), tumour and seminal vesicles against the MOMENTUM image quality assessment criteria (1 = not scanned, 2 = not visible, 3 = not clear, 4 = clear, 5 = very clear), while blinded to the sequence used.
ADC maps (figure 1) were calculated using the b = 150 and 500 s/mm2 images. Structure contours were obtained by rigidly registering the DWI images to the planning MR images, and adapting the contours drawn on the planning MR. Median whole prostate ADC measurements were compared between the two sequences by Bland-Altmann analysis.