Dosimetric comparison of VMAT, fixed-field IMRT and HT for prostate plans using the MADD metric
PO-1800
Abstract
Dosimetric comparison of VMAT, fixed-field IMRT and HT for prostate plans using the MADD metric
Authors: Noelia Suarez Alvarez1,2, Albert Bartrés Salido3, Vicent Pastor i Sanchís4, Nam Nguyen5, Vincent Vinh-Hung6, Melanie Erzilbengoa3
1 Onkologikoa, Medical Physics, Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain; 2Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias, Medical Physics, Oviedo, Spain; 3Onkologikoa, Medical Physics, Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain; 4Onkologikoa, Donostia-San Sebastián, Oviedo, Spain; 5Howard University, Radiation Oncology, Washington,DC, USA; 6University Hospital of Martinique, Radiotherapy, Fort-de-France, Martinique
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Numerous studies have aimed to develop dosimetric indexes that allow to accurately represent the homogeneity of the treatment plan while minimizing time-consuming DVH-based analysis. The recently developed mean absolute dose deviation (MADD) index (Vinh-Hung et al, 2020) has been successfully applied in several breast studies.
The present study aims to re-evaluate eighty prostate treatment plans using a penalty score that weights the mean absolute dose deviations (MADD) for the different structures.
Material and Methods
Eighty prostate cases were retrospectively identified for this study: 22 with 6FFF Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) plans for a Varian TrueBeam STx, 24 Fixed-Field Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (FF-IMRT) plans and 34 plans with Helical TomoTherapy (HT). Radiation doses to rectum, bladder, femoral heads, sigmoid and planned target volume (PTV) were evaluated using the mean absolute dose deviation (MADD). This metric measures how widely the dose delivered to a structure i deviates from a reference dose. That reference dose represents the prescription dose in the case of the target volume and zero for the organs at risk (OAR). The total penalty score sums all the MADD values weighted by a relative factor of w(i).
Calculations were performed with an in-house Matlab R2016 code by importing the treatment planning system (TPS) DVH data.
Results
Figures 1 and 2 summarize the corresponding MADDs for the target and organs at risk. MADD valures are expressed as a percentage of the prescribed dose to make the MADD from the OARs dose-independent since different total dose prescriptions were used.
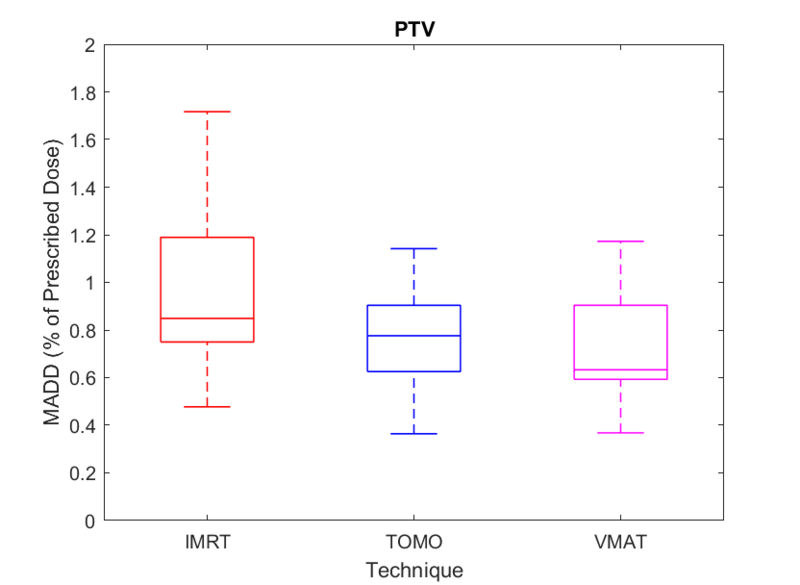
Figure 1
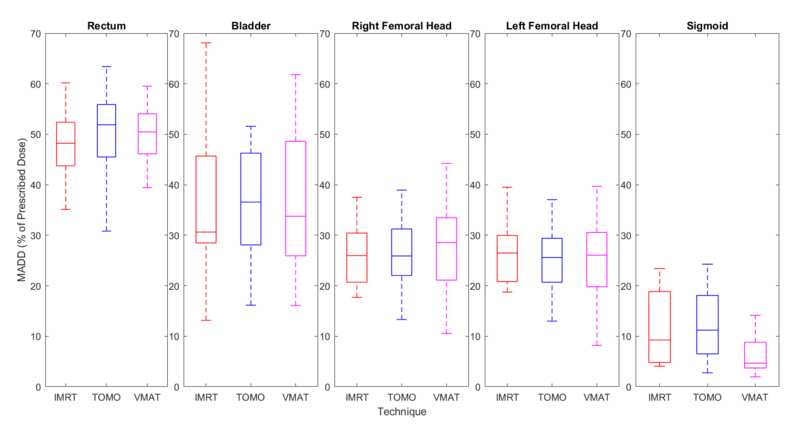
Figure 2
The average MADD value is higher for the FF-IMRT technique (0,96±0,33%) and VMAT and HT techniques achieve the same homogeneity in the target: 0,74±0,29% and 0,75±0,21%, respectively.
By calculating the penalty score with the same relative weight assigned to all structures, HT achieved the lowest index value (26.4±6,1%), indicating that HT showed better OARs sparing.
Conclusion
The penalty score based on the mean absolute dose deviation has proven to be a useful tool to evaluate the DVH and whose results agree with previous works.
Both VMAT and HT can provide more uniform target doses as compared to F-F IMRT. Helical TomoTherapy is superior to IMRT and VMAT in preserving OARs and planning quality parameters, as previous studies have shown (Rao et al,2010).