Framework for out-of-field dosimetry in photon radiotherapy: application to Hodgkin lymphoma
Maite Romero-Expósito,
Sweden
PO-1783
Abstract
Framework for out-of-field dosimetry in photon radiotherapy: application to Hodgkin lymphoma
Authors: Maite Romero-Expósito1, Maite Romero-Expósito2, Isidora Muñoz3, Ignacio López-Martínez3, Ignacio Espinoza3, Iuliana Toma-Dasu4,5, Alexandru Dasu1,6, Daniel Molin7, Beatriz Sánchez-Nieto3
1The Skandion Clinic, -, Uppsala, Sweden; 2Karolinska Institutet, Oncology Pathology Department , Stockholm, Sweden; 3Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Instituto de Física, Santiago, Chile; 4Karolinska Institutet, Oncology Pathology Department, Stockholm, Sweden; 5Stockholm University, Medical Radiation Physics, Stockholm, Sweden; 6Uppsala University, Medical Radiation Sciences, Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala, Sweden; 7Uppsala University, Experimental and Clinical Oncology, Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala, Sweden
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The improved outcome of radiotherapy (RT) treatments raises the awareness of long terms effects, such as secondary cancers. This is of special interest for young patients, treated with a curative intent, a group where classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is common. The objective of this work is to present the implementation of a framework for cHL patients to evaluate the out-of-field doses related to secondary cancer risk.
Material and Methods
The system consists of 2 integrated Matlab-based programs to process the dicom files of a RT plan exported from the TPS. The first program, IS²aR (Rad. Oncol. 2022;170:S1341-S1342), generates a virtual whole-body CT phantom using the original CT of the patient, which covers only a small volume of the patient around the target, as an input. This program registers the patient CT with the reference phantoms from ICRP-110. The second program, Periphocal 3D (P3D), has implemented the analytical model by Sánchez-Nieto et al (Front. Oncol. 2022;12:872752) to evaluate peripheral photon dose in the virtual phantom from the number of MU, the prescription dose, the mean field (from 50% isodose) and the out-of-field area (defined from the 5% isodose). With all these inputs, P3D calculates the DVHs of the organs delineated on the ICRP-110 that falls in the out-of-field area. The system was tested in cHL patients, treated with VMAT.
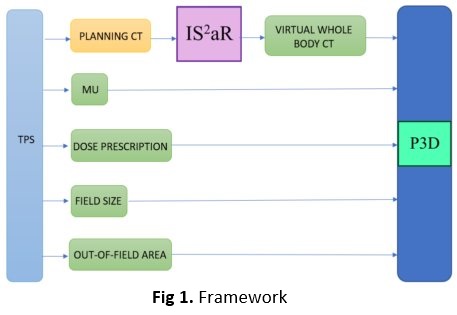
Results
The registration process and generation of the virtual phantom took most of the overall time, between 15 and 25 minutes, for the patients considered. The dice coefficient was calculated to evaluate the registration, obtaining values between 0.5 and 0.6 for the patients considered (these values mean an acceptable agreement for a whole-body rigid registration). The calculation of out-of-field doses with P3D took less than 5 minutes. Even though cHL targets can present a wide variation depending on the patient, the calculated doses were not much different, being within the uncertainties of the model in the out-of-field area. For example, the mean dose to oesophagus and liver were found in the intervals 20-25 mGy/Gy and 1.5-1.7 mGy/Gy, respectively.
Conclusion
A successful implementation of the general framework for cHL patients undergoing VMAT was carried out. The system represents a valuable tool for out-of-field dosimetry, providing organ doses within about 30 minutes per patient. DVHs provided by the computation platform can be subsequently used for secondary cancer risk estimations.