A novel anthropomorphic surrogate for advanced QA in stereotactic adaptive radiotherapy deliveries
PO-1743
Abstract
A novel anthropomorphic surrogate for advanced QA in stereotactic adaptive radiotherapy deliveries
Authors: Mathias Dierl1, Michael Robinson2, Mark Rose2, Andreas A. Schönfeld3, Ndimofor Chofor3
1Klinikum Bayreuth GmbH, Department of Radiation Therapy, Bayreuth, Germany; 2Sun Nuclear, A Mirion Medical Company, Product Strategy, Melbourne, USA; 3Sun Nuclear, A Mirion Medical Company, Research and Development, Melbourne, USA
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Adaptive radiotherapy (ART) quality assurance (QA) requires the utilization of phantoms and detector combinations capable of tracking and accounting for deviations from the initially planned treatment configuration. To enhance the capabilities of the SRS MapCHECK in ART QA for stereotactic deliveries, a new add-on surrogate has been tested for the StereoPHAN. In this study, we investigated the surrogate’s (i) influence on the dose distribution within the treatment planning system (TPS) and the dosimetric verification with the SRS MapCHECK, (ii) detectability of the surrogate and its use in combination with a VisionRT surface-guided radiotherapy system and (iii) its usage in combination with the Dynamic Platform model 008PL (Sun Nuclear, A Mirion Medical Company, Norfolk, USA) to enhance gated dose deliveries.
Material and Methods
The anthropomorphic surrogate under investigation, see Figure 1, was designed to fit onto the StereoPHAN, which typically houses the SRS MapCHECK (both Sun Nuclear, A Mirion Medical Company, Melbourne, USA). CTs were obtained for the same setup with and without the anthropomorphic surrogate in place to assess adequate density overwrites for the TPS. Typical clinical plans comprising of an open static field and an open arc, each of 4 × 4 cm², were delivered and investigated for both setup configurations, with results evaluated in SNC Patient. Next, the capability of the system to enhance surface guidance deliveries was evaluated in combination with a VisionRT system. Following prior setup using the XVI imager, the misalignment of the hexapod tabletop at a Versa HD linac (Elekta AB, Stockholm, Sweden) was tracked using the VisionRT system. Finally, we tested the applicability of the system to facilitate gated beam deliveries using the Dynamic Platform model 008PL in combination with surface guidance.
Results
Using global gamma 3 % / 3 mm at 10 % dose threshold, delivered clinical plans had passing rates higher than 98 % after implementing a homogeneous density overwrite for the anthropomorphic surrogate within the TPS. The VisionRT system correctly tracked the misalignment of the setup within sub-millimeter accuracy in all directions, indicating the suitability of the surrogate towards enhancing surface guidance QA. Gated beam deliveries were also feasible with the surrogate in place.
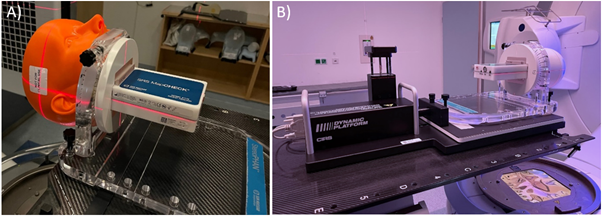
Figure 1: (a) Anthropomorphic surrogate mounted on StereoPHAN and (b) Setup on motion platform, prior to surrogate placement, to investigate SGRT and gated dose deliveries.
Conclusion
The anthropomorphic surrogate enhances the use of the StereoPHAN in combination with the SRS MapCHECK towards quality assurance and end-to-end tests in stereotactic deliveries. The excellent detectability of the surrogate extends the applicability towards surface guidance and gated radiotherapy deliveries.