Autoplanning tangential IMRT technique for DIBH breast radiotherapy: a robustness evaluation.
PO-2029
Abstract
Autoplanning tangential IMRT technique for DIBH breast radiotherapy: a robustness evaluation.
Authors: Alessio Gnerucci1, Marco Esposito2, Alessandro Ghirelli2, Silvia Pini2, Lisa Paoletti3, Raffaella Barca3, Simona Fondelli3, Paolo Alpi3, Barbara Grilli3, Francesca Rossi4, Silvia Scoccianti3, Serenella Russo2
1University of Florence, Physics and Astronomy, Florence, Italy; 2Azienda USL Toscana Centro, Medical Physics Unit, Florence, Italy; 3Azienda USL Toscana Centro, Radiotherapy Unit, Florence, Italy; 4Azienda USL Toscana Sud Est, Radiotherapy Unit, Grosseto, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Aim of the work is to evaluate the robustness of an autoplanning tangential IMRT technique adopted in DIBH Surface Guided Radiotherapy (SGRT) of left breast cancer. The dosimetric effects on OARs constraints and target volume coverage, due to the residual intrafraction movements allowed by the motion tolerances, was investigated.
Material and Methods
A sample of 12 SGRT DIBH left breast treatments for a total of 192 fractions were analyzed. C-RAD Sentinel™ laser scanning system and a Siemens CT scanner were used for the prospective DIBH CT study. Base line and gating window levels (5mm amplitude) were established during CT simulation procedure. Gated treatments delivery (5mm shift threshold) was supported by the C-RAD Catalyst™ system connected with an Elekta Synergy. Planning was performed with an autoplanning tangential IMRT technique implemented in TPS Pinnacle3 v.16.2 for a dose prescription of 42.56 Gy in 16 fractions. The average of the real time isocenter displacement (SGRT shift) between the live surface and the daily reference surface during beam delivery was evaluated for each treatment fraction by analyzing the three-dimensional motion data in the log files of the optical system. Then, the perturbed dose distribution was calculated by applying this average fraction shift to the original plan isocenter. The total plan dose distribution was finally obtained by accumulating the fractions perturbed doses. The original plan and the perturbed one calculated for each patient were compared by means of Wilcoxon test on target coverage and OARs dose DVH metrics. In addition, the overall decrease in the plan quality was studied by evaluating a plan global quality indicator based on the dosimetric scoring of target coverage and OAR sparing.
Results
The residual intrafraction movements showed a Lateral cumulative distribution consistent with a null shift, whereas Longitudinal and Vertical ones were slightly negative (mean values <1 mm). The cumulative effect on the dose distributions of all treatment fractions was slight without any significant variations between the original and the perturbed plan target coverage and OARs DVH metrics. The variations resulted lower than 0.4 Gy for Dose metrics and 0.4% for volume metrics (fig.1). Moreover, none of the perturbed plans showed DVH metrics exceeding the mandatory constraints. The global plan quality analysis confirmed that, for this technique, the residual isocenter shifts did not worsen the plan significantly (fig.2).

Fig.1
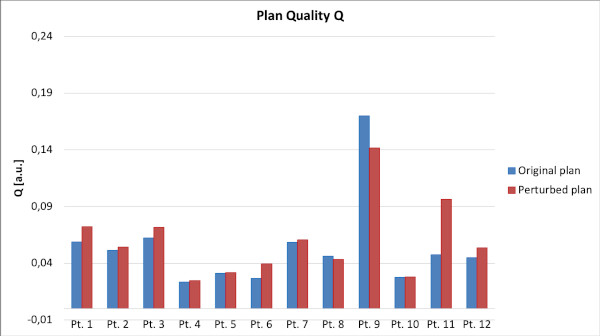
Fig. 2.
Conclusion
The presented autoplanning tangential IMRT technique for DIBH SGRT proved to be robust against residual intrafraction isocenter shift with no significant deteriorations in the perturbed plans and no DVH metrics exceeding the mandatory constraints for all the 12 perturbed plans investigated.