Dosimetric indexes and its potential relationship with target size and location in SBRT lung cancer.
Sandra Guardado Gonzalez,
Spain
PO-2061
Abstract
Dosimetric indexes and its potential relationship with target size and location in SBRT lung cancer.
Authors: GUSTAVO POZO RODRIGUEZ1, SANDRA FERNÁNDEZ ALONSO2, SANDRA GUARDADO GONZALEZ3, EDUARDO CABELLO MURILLO1, ANA MILANÉS GAILLET1, PEDRO ADAIMI HERNÁNDEZ1, RAÚL DÍAZ FUENTES1, MARTA MANZANO RODRÍGUEZ1, ÁNGEL GAITÁN SIMÓN1, ALEJANDRO FERRANDO SÁNCHEZ1, PALOMA BOTELLA FAUS4, PAULA GARCÍA CASTAÑÓN5, DANIEL ROJO NAVARRETE1, JOSÉ FERMÍN PÉREZ-REGADERA GÓMEZ3
1H.U. 12 DE OCTUBRE, MEDICAL PHYSICS, MADRID, Spain; 2H.U.12 DE OCTUBRE, RADIATION ONCOLOGY, MADRID, Spain; 3H.U. 12 DE OCTUBRE, RADIATION ONCOLOGY, MADRID, Spain; 4H.U.12 DE OCTUBRE, MEDICAL PHYSICS, MADRID, Spain; 5H.U. LA PRINCESA, MEDICAL PHYSICS, MADRID, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
To evaluate a potential correlation between Paddick (PI) and Gradient (GI) indexes (as defined in ICRU report 91) for lung SBRT treatments against target location within the lung and ITV .
Material and Methods
A cohort of 159 lung patients that have undergone SBRT therapy since 2016 have been classified into seven groups regarding its location (table I). Dose to the target has followed an adaptive risk strategy aimed to a minimum BED>100Gy in 90.0% of cases analysed.
SBRT treatments were performed on a Varian Clinac 2300 iX. This linear accelerator includes an On Board Imager unit to perform KVCBCT and a Millenium 120 MLC (5mm thickness at isocenter) for treatments performance (Varian Medical Systems, (VMS)).
Treatment Planning System used for clinical dosimetry was Eclipse 15.6, and two algorithms available: Acuros 15.6 and AAA 15.6 (Analytical Anisotropic Algorithm) configured with a 2.5 mm calculation grid . PO 15.6 optimizer was used for VMAT treatments (VMS).
4DCT was acquired with Philips Brilliance CT, using a nominal slice thickness of 2mm. Respiratory cycle was binned into 10 phases and ITV was generated by means of merging 10 segmented GTV.
Three partial arcs were used from 0° to 180° with collimation angles set to 30°, 330° and 30°, respectively. Photon energy was set to 6MV and isodose prescription ranged from 110% to 125%.
Results
Statistical analysis with Stata v.16 (StataCorp.) has been carried out to assess PI and GI correlation with: target lateral location (left/right), transversal location (grouped in three categories: chest wall (CW), centered (C) and ‘Others’ (O)); and ITV volume.
Paddick Index.
Positive association between ITV volume and PI has been found (p-value<0.0001), with an average slope of 0.0018 cm˜³.
Neither lateral nor axial location has brought significant correlation.
Gradient Index.
When comparing with main location (CW), ‘Others’ shows a lower GI (p-value=0.017), with an averaged difference of 0.250. GI of CW and C categories had no significant differences.
In addition, no significant differences have been found between lateral location and GI (p-value=0.277).
Negative association between ITV volume and GI has been observed (p-value<0.0001).
Table I.
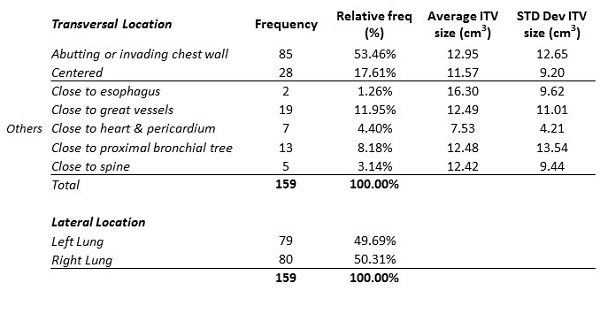
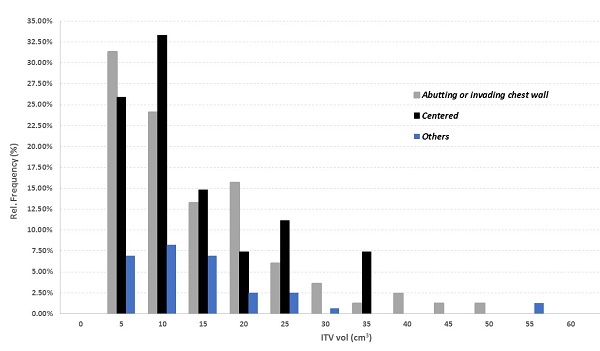
Figure I. ITV size distribution.
Conclusion
Statistical analysis reveals some behaviors connected to target location and size.
Paddick Index:
Since PI is defined <1, the higher the ITV volume the better tends to be PI according to an average slope of 0.0018 cm-3 (p-value<0.0001).
Gradient Index:
Conversely, increasing ITV volume seem to display a negative association with GI (p-value<0.0001), defined as the ratio of volume isodose of 50% and 100%, that is, the higher the ITV volume the steeper the dose distribution in our study.
GI associated with ‘Others’ category exhibits a lower value when comparing to GI linked to CW (p-value=0.017), with an averaged difference of 0.250 and hence a better dosimetric fall-off.