Scalp or face angiosarcoma treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy, a multicenter study
PO-1552
Abstract
Scalp or face angiosarcoma treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy, a multicenter study
Authors: Takahiro Iwai1, Toshiyuki Imagumbai2, Shinya Hiraoka1, Takahiro Kishi3, Shun Okabayashi1, Ryo Ashida2, Takamasa Mitsuyoshi2, Yukinori Matsuo1, Takashi Ishigaki3, Takashi Mizowaki1, Masaki Kokubo2
1Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Radiation Oncology and Image-applied Therapy, Kyoto, Japan; 2Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Kobe, Japan; 3Osaka Red Cross Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Osaka, Japan
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Scalp or face angiosarcoma is a rare cutaneous malignancy with a poor prognosis. Combined therapy including whole scalp radiotherapy (RT) is the treatment for scalp or face angiosarcoma, and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is considered to have benefits for target coverage and shorter treatment time. We reviewed the patients with scalp or face angiosarcoma treated with VMAT at several institutions.
Material and Methods
Between January 2015 and March 2020, patients with scalp or face angiosarcoma without distant metastasis treated with VMAT at three institutions were evaluated. Both definitive RT and postoperative RT were included. Information regarding patient status, tumor characteristics, treatment characteristics, and outcomes were obtained from the clinical records. Local control probability (LC), overall survival (OS), and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method from the start date of any first treatment for angiosarcoma. Toxicity was evaluated by CTCAE version 5.0.
Results
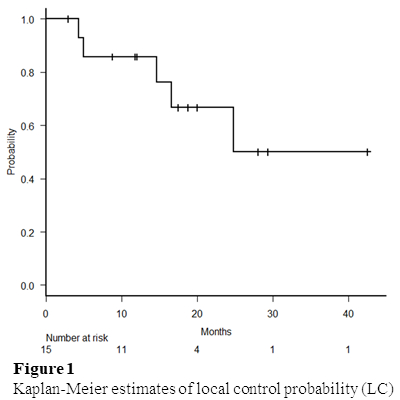
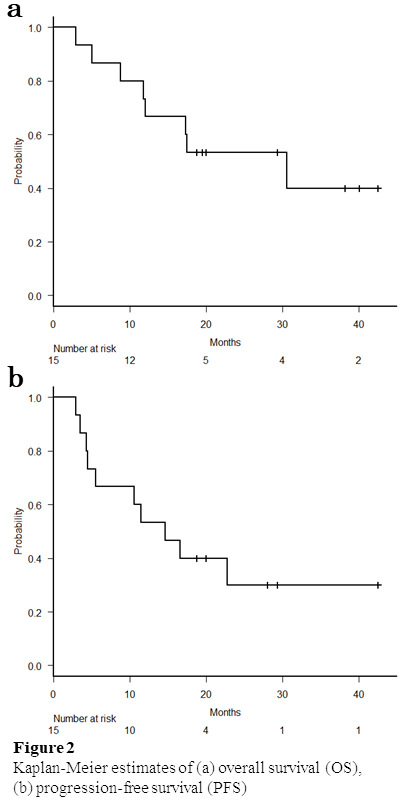
Fifteen patients, 5 patients each from three institutions were included in this study (Table 1). Definitive RT and postoperative RT was performed for 10 and 5 patients. Surgical excision was performed with a 0-2 cm margin. Besides 1 patient, all patients were treated with VMAT; 2-4 arcs with 4 MV or 6 MV photons. One patient was treated with VMAT and electron boost. The frequent dose and fractions were 70Gy in 35 fractions. The clinical target volume (CTV) was whole scalp for 11 patients, whole scalp plus prophylactic lymph node for 3 patients, and extended primary site for 1 patient. The planning target volume (PTV) was CTV with a margin of 3-5 mm in all directions. Induction, concurrent, and maintenance systematic therapy was administered for 9, 14, and 12 patients. The most frequent regimen of systematic therapy was weekly paclitaxel. The median follow-up time was 15.7 months and 8 patients were alive at analysis. The one-year LC was 86% (Figure 1). The one-year OS and PFS were 66.7% and 53.3% (Figure 2). Recurrence was observed in 9 patients; 5 patients had local recurrence, and 7 patients had distant metastasis. For acute non-hematologic toxicity, grade 3 dermatitis, mucositis, and hyponatremia occurred for 12, 1, and 1 patients. For late toxicity, grade 3 and 5 skin ulceration was observed in 4 and 1 patients. The patient with grade 5 skin ulceration died because of infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa from ulceration. Any other grade 3 or higher non-hematologic toxicities were not observed.
Table 1 Patient and tumor characteristics
Characteristics
| no.
| %
| median (range)
|
Age (years)
|
|
| 74 (66-90)
|
Sex Male Female
|
10
5
|
66.7
33.3 |
|
Tumor diameter (cm)
|
|
| 9.5 (1.7-33.0)
|
Tumor location Scalp
Face
|
14
1
|
93.3
6.7
|
|
Skip lesions Yes
No
|
8 7 |
53.3 46.7 |
|
With ulcerative lesions Yes No |
5 10 |
33.3 66.7 |
|
With nodule lesions Yes No |
11 4 |
73.3 26.7 |
|
With muscle invasion Yes No |
2 13 |
13.3 86.7 |
|
Lymph node metastasis Yes No |
2 13 |
13.3 86.7 |
|
Conclusion
The outcome of the patients with scalp or face angiosarcoma treated with VMAT was acceptable.