Preliminary toxicity data on Trastuzumab emtansine and concomitant radiotherapy in adjuvant setting
Carola Maria Elisa Perotti,
Italy
PO-1288
Abstract
Preliminary toxicity data on Trastuzumab emtansine and concomitant radiotherapy in adjuvant setting
Authors: Carola Maria Elisa Perotti1, Donata Sartori2, Costanza De Rossi3, Laroussi Lamin1, Imad Abu Rumeileh1
1Ospedale dell'Angelo, Radiotherapy Department, Venezia - Mestre, Italy; 2Ospedale di Mirano e Dolo, Department of Medical Oncology , Mirano (VE), Italy; 3Ospedale dell'Angelo, Department of Medical Oncology, Venezia - Mestre, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The use of Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in the adjuvant setting in patients with residual HER2-positive breast cancer after neoadjuvant treatment was approved in Italy less than two years ago.
The purpose of our retrospective analysis is to evaluate the toxicity of this drug when administered concomitantly with adjuvant radiotherapy treatment.
We observed in particular the possible correlation between radiotherapy dose to the target volume and to the organs at risk and specific toxicities.
Material and Methods
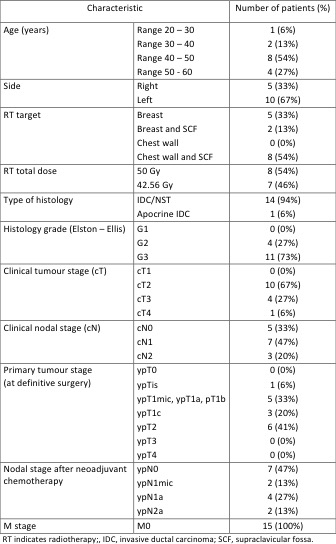
Fifteen patients were treated with concomitant T-DM1 and radiotherapy between December 2020 and July 2022. A CT scan of the chest and a left ventricular ejection fraction assessment were performed at baseline and after radiotherapy. The Common Terminology Criteria of Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 3.0 was used to evaluate toxicity.
Results
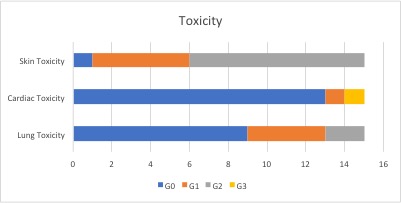
The mean age was 46 years (range 27 to 69), radiotherapy was delivered to the left breast/chest wall in 10 cases and to the right in 5. In 10 cases the lymph nodes were irradiated, 8 patients received radiotherapy to the chest wall. The total delivered dose was 50 Gy in 25 fractions in 8 patients and 42.56 Gy in 16 fractions in 7 patients. The mean ipsilateral lung dose was on average 7.3 Gy (range 1.4 Gy to 12.2 Gy), the mean heart dose in left breast/chest wall patients was on average 2.2 Gy (range 1.2 Gy to 3.3 Gy). Grade 2 lung toxicity was observed in 2 patients, G1 in 4 patients; one patient experienced a G3 left ventricular ejection fraction decrease which required T-DM1 discontinuation. Nine patients developed G2 skin toxicity after radiotherapy, 5 developed G1 skin toxicity.
Conclusion
Our retrospective analysis showed a good tolerability profile in terms of skin and cardiac toxicity. Interesting data are those related to pulmonary toxicity in concomitant treatment, which in our cohort of patients appears to correlate with a mean dose to the ipsilateral lung equal or higher than 8 Gy. Further investigation and prospective data are needed to better investigate this aspect.