Previous Irradiation Impairs the DNA DSB Repair System in Sheep Lung-Derived Epithelial Cells.
MO-0723
Abstract
Previous Irradiation Impairs the DNA DSB Repair System in Sheep Lung-Derived Epithelial Cells.
Authors: Larry Bodgi1,2, Joelle Al-Choboq1, Joyce Azzi1, Jolie Bou Gharios1, Charbel Feghaly1, Rafka Challita1, Hanine Bou Hadir1, Fabienne Abi Antoun1, Luna Dib1, Mustafa Jammal1, Farah Olleik1, Tarek Araji3, Phillip Taddei4, Fady Geara1, Laura Dosch5, Pierre Sfeir6, Abdo Jurjus2, Wassim Abou Kheir2, Bassem Youssef1
1American University of Beirut Medical Center, Radiation Oncology, Beirut, Lebanon; 2American University of Beirut, Anatomy, Cell Biology and Physiological Sciences, Beirut, Lebanon; 3American University of Beirut, Anatomy, Cell biology and Physiological Sciences, Beirut, Lebanon; 4Mayo Clinic, Radiation Oncology, Rochester, USA; 5American University of Beirut Medical Center, Faculty of Medicine, Beirut, Lebanon; 6American University of Beirut Medical Center, Surgery, Beirut, Lebanon
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Childhood cancer survivors who receive early radiotherapy (RT) treatments face the likelihood of long-term effects from their treatment that can be debilitating, chronic, and even fatal. One of these late effects that bear the greatest concern is the development of a second radiogenic cancer. In fact, irradiating normal tissues can cause mutations that might affect the DNA damage repair pathways, proto-oncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes, which enhances the risk of secondary cancer.
In order to mimic pediatric craniospinal irradiation, a sheep regiment (5 treated, 4 controls) was treated with radiation administered to the thecal sac. However, incidental irradiation was also delivered to nearby tissues.
The purpose of this project is to study the effect of previous RT on the DNA double-strand breaks repair kinetics. Three years after receiving the treatment, biopsies from lung tissues exposed to low and high doses of X-rays were tested and compared for treated and untreated sheep.
Material and Methods
A total of 9 sheep, 5 treated and 4 control, were included in this study. The treated sheep received a total dose of 28 Gy, administered in 8 sessions, targeting their spinal thecal sac. Treatment areas were divided into two regions, depending on the received dose: high dose (HD, dose> 20 Gy) and low dose (LD, dose <2 Gy). Three years after their treatment, lung biopsies were taken from the HD, LD areas and from the control untreated sheep. Lung epithelial cells were derived, cultured and amplified. This study included 5 control, 4 LD, and 4 HD primary lung epithelial cells.
After amplification, cells were irradiated with a 2 Gy dose, and the kinetics of DNA DSB repair was assessed through anti-γH2AX and anti-pATM immunofluorescence. The number of foci was assessed without re-irradiation, and 10 min, 1h, 4hrs, and 24hrs after irradiation. A non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was performed to compare the values between the control, LD, and HD cell lines.
Results
Without any irradiation, both LD (1.8 ±0.5 foci, p<0.05) and HD (1.55±36 foci, p<0.01) cells had a significantly higher number of spontaneous γH2AX foci when compared with the control (0.7±0.1 foci). 10 mins after a 2 Gy re-irradiation, only LD cells had a significantly lower number of foci (49 ± 1.6 foci) than the control (60.7±1.8 foci). Interestingly, the number of residual foci 24 hrs after irradiation was higher for both LD (5.7±0.9 foci, p<0.01) and HD (7.25±1 foci, p<0.01) when compared with the cells provided from the non-irradiated sheep (2.1±0.3 foci). Finally, LD and HD cells had a lower number of pATM foci 10 mins after 2 Gy (p<0.01) when compared with the control cell line.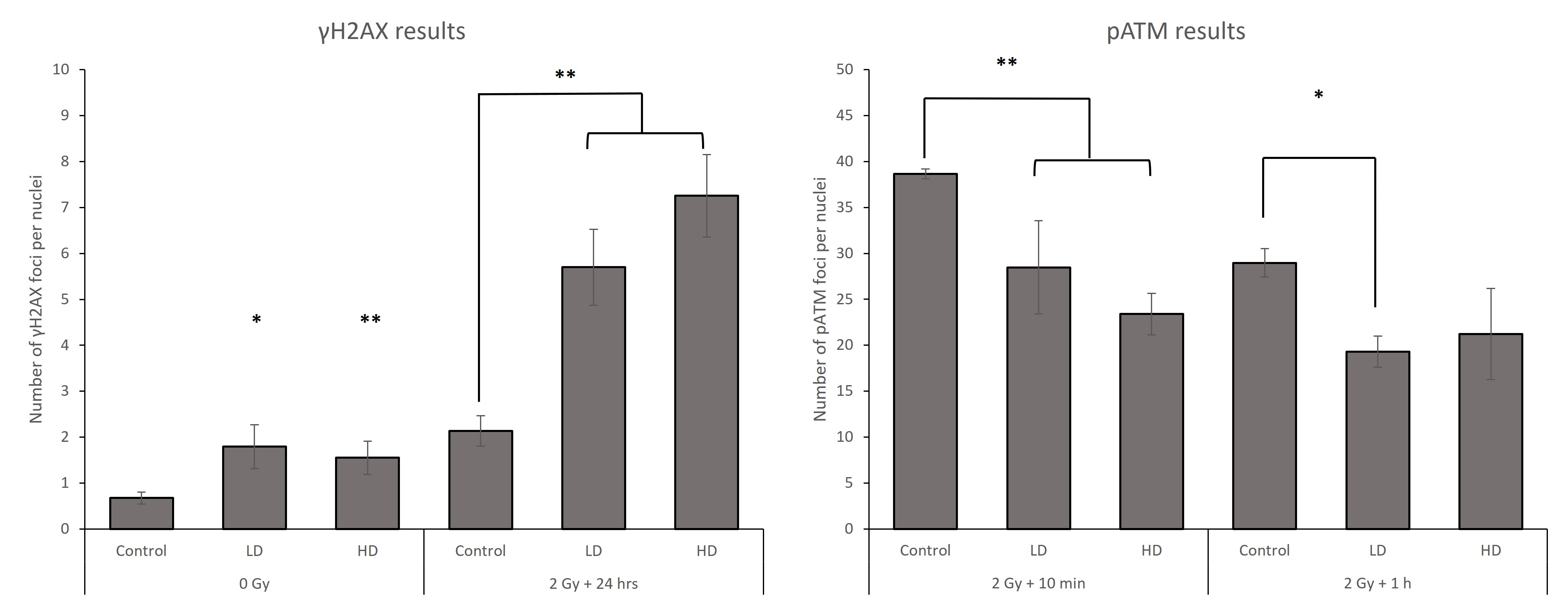
Conclusion
Our results show that, on the long term, previous irradiation of normal tissues can 1) increase the genomic instability; 2) decrease the efficiency of DNA DSB signaling, and 3) decrease the efficiency of DSB repair, in primary cell lines derived from sheep lung epithelial tissues.