Experimental characterization of two novel MR-conditional ionization chambers in magnetic fields
Moritz Schneider,
Germany
MO-0673
Abstract
Experimental characterization of two novel MR-conditional ionization chambers in magnetic fields
Authors: Moritz Schneider1, Stephan Frick2, Marcel Nachbar1, Ralf-Peter Kapsch2, Daniela Thorwarth1
1University Hospital and Medical Faculty, Eberhard Karls University Tuebingen, Department of Radiation Oncology, Section for Biomedical Physics, Tuebingen, Germany; 2Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), 6.21 Dosimetry for radiotherapy, Braunschweig, Germany
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The availability of real-time MRI allows for online motion management in MRgRT. So far, ionization chambers generated artifacts in MRI, potentially irritating gating algorithms and obstructing the use of MRI for dosimetry and QA of MRgRT.
In this work we investigated the dosimetric characteristics of two novel ionization chambers, Semiflex3D-MR (PTW31024) and PinPoint3D-MR (PTW31025), specifically developed for artifact-free usage in MR-Linacs.
Material and Methods
To investigate the chamber readings for various magnetic flux densities 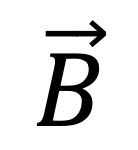 and beam qualities, measurements were done in a water phantom using a standard linac (Elekta Precise) with an electromagnet insert. The ionization chambers were placed in 10 cm water equivalent depth, with their chamber axis perpendicular to the magnetic field. One response curve per chamber type was acquired once for 6 MV, with
and beam qualities, measurements were done in a water phantom using a standard linac (Elekta Precise) with an electromagnet insert. The ionization chambers were placed in 10 cm water equivalent depth, with their chamber axis perpendicular to the magnetic field. One response curve per chamber type was acquired once for 6 MV, with  .
.
The correlation of chamber response and beam quality was determined for 6, 10 and 15 MV and 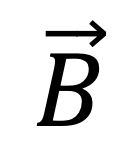 = 0.35 and 1.5 T. Those measurements were repeated three times.
= 0.35 and 1.5 T. Those measurements were repeated three times.
Magnetic field correction factors 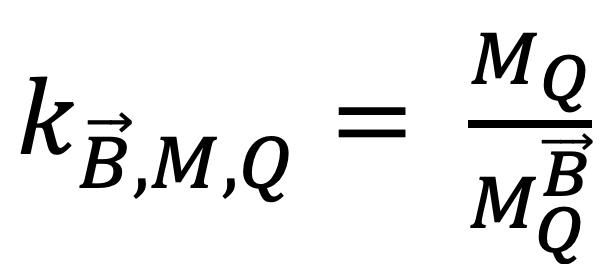 were assessed by doing five independent measurements for five chambers of each type for 6 MV and 0.35/1.5 T.
were assessed by doing five independent measurements for five chambers of each type for 6 MV and 0.35/1.5 T.
The influence of rotating the chamber axis was evaluated by deriving  , which was measured five times for two chambers of each type at the 1.5 T MR-Linac (Elekta Unity).
, which was measured five times for two chambers of each type at the 1.5 T MR-Linac (Elekta Unity).
Results
Both chamber types showed a continuous response curve with decreasing response for increasing absolute magnetic flux densities. The decrease of response is higher for both chambers, if the Lorentz force points to the tip of the chamber (fig.1).
Both types of ionization chambers showed a linear dependency on the beam quality (R2 > 0.99 for = 0.35/1.5 T).
The five Semiflex3DMR chambers showed consistent results with mean = 1.0470±0.0014 (STD) and = 1.0000±0.0005 for 1.5 and 0.35 T respectively. The PinPointMR chambers showed increased deviations (fig.2), was observed as 1.0427±0.0051 (1.5T) and 1.0043±0.0022 (0.35T).
At the 1.5 T MR-Linac, crot was determined as 0.9412±0.0019 (PTW31024) and 0.9600±0.0023 (PTW31025). Using , crot, the linear interpolation between beam qualities and from literature [1], was determined to be 1.051±0.004/0.989±0.005 for PTW31024 and 1.050±0.007/1.008±0.007 for PTW31025 in perpendicular, respectively anti-parallel orientation.
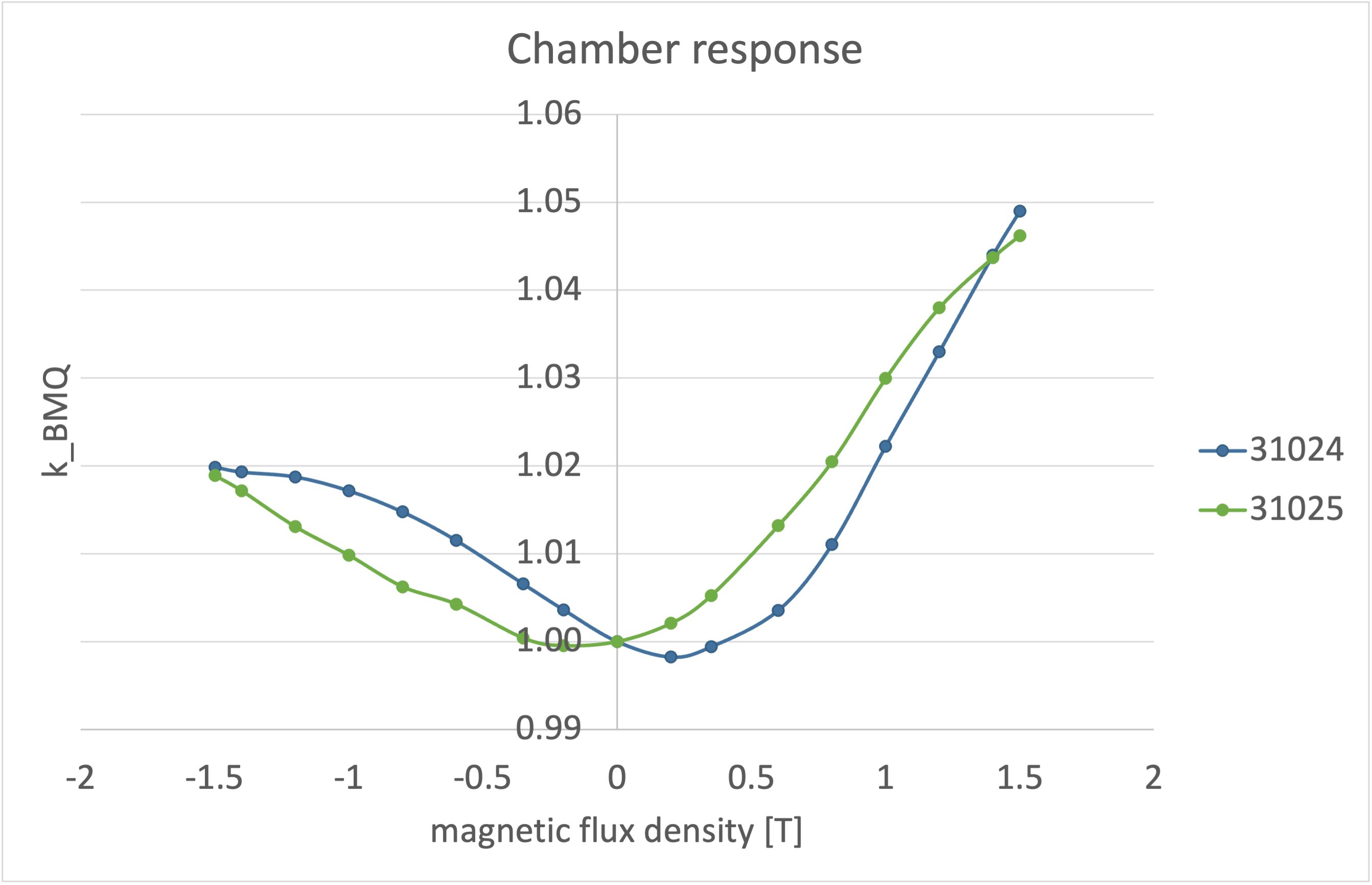
Figure 1: Effect of variating magnetic flux densities on the chamber readings.
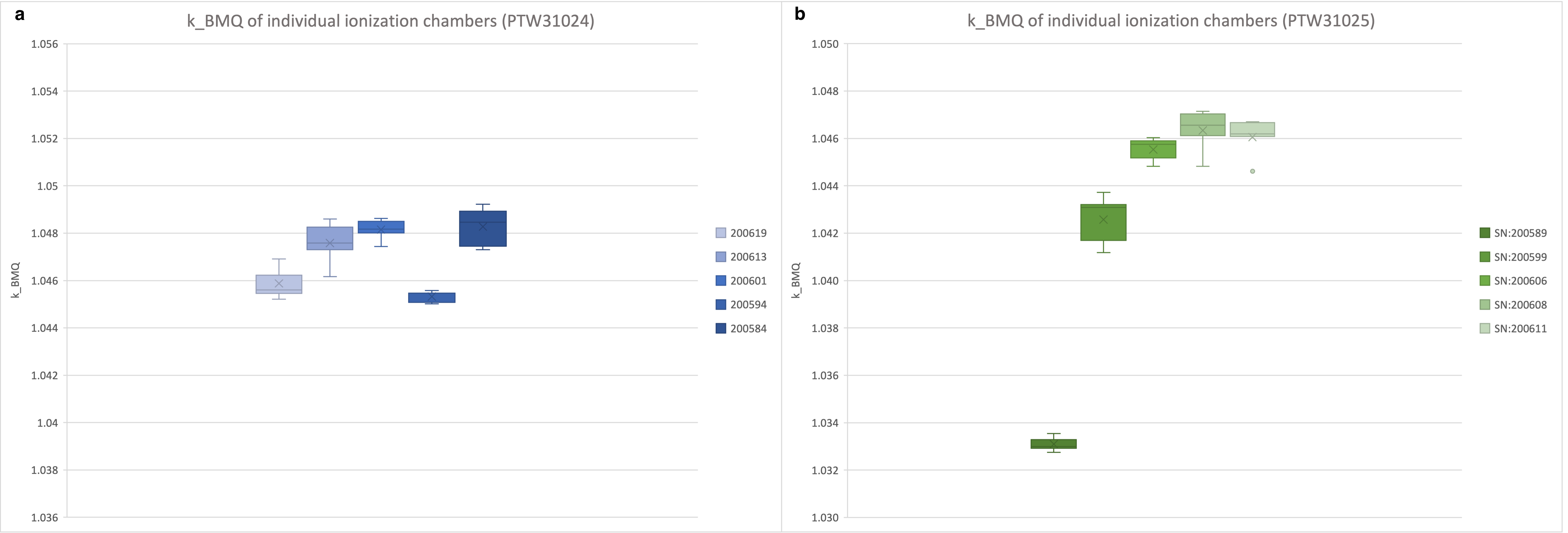
Figure 2: 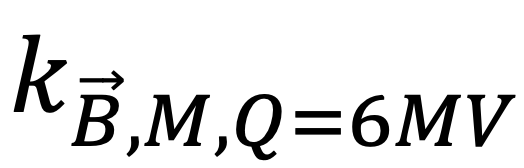 for all individual chambers included in this work, a) Semiflex3D-MR, b) PinPoint3D-MR.
for all individual chambers included in this work, a) Semiflex3D-MR, b) PinPoint3D-MR. 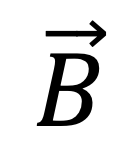 was 1.5 T
was 1.5 T
Conclusion
The dosimetric behavior of two novel MR-conditional ionization chambers was investigated. In case of PTW31024, all chambers showed consistent results, leading to small uncertainties in the observed correction factors. The PTW31025 chambers we used showed larger uncertainties due to one chamber showing deviating results, potentially indicating intra-type variations and emphasizing the need to cross-check new ionization chambers.
References:
[1] Pojtinger S et al. PMB 2020